Lesson one
Oral topic: our university
| Grammar: | The System of the English Tenses (Active). The Word Order. |
Part I
Vocabulary Learning
Exercise 1. Запомните следующие слова:
| 1. | accommodation n. [ә,kɔmә′deıʃ ә n] – жилье; |
| 2. | arrange v. [ә′reın dʒ ] – организовывать, устраивать; |
| 3. | assist v. [ә′sıst] – помогать, содействовать; |
| 4. | assistant n. [ә′sıst ә nt] – ассистент, помощник; |
| 5. | associate professor n. [ә′sәuʃııt prә′fesә] – доцент; |
| 6. | attend v. [ә′tend] – посещать, присутствовать (на лекциях, занятиях и т.п.) |
| 7. | award (be awarded) v. [ә′wɔ:d] – награждать; |
| 8. | be in charge of [ʧα:dʒ] – руководить; |
| 9. | be responsible for [rıs′pɔnsәbl] – быть ответственным за; |
| 10. | chemist’s (shop) n. [′kemısts] – аптека; |
| 11. | continuous education [kәn′tın j uәs,edju(:)keıʃәn] – непрерывное образование; |
| 12. | day-time n. [′dәıtaım] – дневной; |
| 13. | deliver (lecture) v. [dı′lıvә] – читать лекцию; |
| 14. | department n. [dı′pα:tmәnt] – отделение, кафедра; correspondence ~ – заочное отделение; |
| 15. | development n. [dı′velәpmәnt] – развитие; |
| 16. | disposal n. (at one’s ~) [dıs′pәuz ә l] – распоряжение (в чьем-либо ~); |
| 17. | edition n. [ı′dıʃ ә n]– издание; |
| 18. | educational manufacturing adj. [,edju(:)’keıʃәnl,mænju′fækʧәrıη] – учебно-производственный; |
| 19. | equipment n. [ı′kwıpmәnt] – оборудование; |
| 20. | experience n. [ıks′pıәrıәns] – опыт; |
| 21. | faculty n. [′fæk ә ltı] – факультет; |
| 22. | guide v. [gaıd] – руководить; |
| 23. | head n. [hed] – глава, руководитель; |
| 24. | hostel accommodations n. [′hɔstәl ә,kɔmә′deıʃ ә n] – жилье в общежитии; |
| 25. | instruct v. [ın′strʌkt] – обучать; |
| 26. | merit n. [′merıt] – заслуга; |
| 27. | pharmaceutist n. [,fα:mә′sju:tıst] – фармацевт; |
| 28. | physician n. [fı′zıʃ ә n] – врач; |
| 29. | practical skills [′præktıkәl ′skılz] – практические навыки; |
| 30. | recreational [,rekrı′eıʃәnl] – развлекательный; |
| 31. | research n. [rı′sә:ʧ] – исследование; |
| 32. | stomatologist n. [,stɔmә′tɔlәdʒıst] – стоматолог; |
| 33. | surgeon n. [′sә:dʒ ә n] – хирург; |
| 34. | teaching staff ['ti:ʧɪŋ stʌf] – штат преподавателей; |
| 35. | train v. [treın] – готовить, обучать; |
| 36. | master v. ['mɑ:stə] – овладевать (языком); |
| 37. | facilities n. [fə'sɪlətɪz] – благоприятные условия; |
| 38. | activity n. [æk'tɪvətɪ] – деятельность; social activities – культурно-просветительские мероприятия; |
| 39. | faculty for advanced training [əd'vɑ:nst] – факультет повышения квалификации. |
Exercise 2. Прочитайте слова. Обратите внимание на орфографию слов латино-греческого происхождения. Переведите их.
Pharmacy [′fαmәsı], pharmaceutical [,fα:mә′sju:tıkl], medicine [′medısın], medical [′medıkl], laboratory [lә′bɔrәtәrı], student ['stju:dənt], professor [prə'fesə], institution [,ɪnstɪ'tju:ʃən], department [dɪ'pɑ:tmənt], general ['ʤenərəl], education [,edju:keɪʃən], instructor [ɪn'strʌktə], stomatology [,stɔmə'tɔləʤɪ], specialist ['speʃəlɪst], university [,ju:nɪ'və:sɪtɪ], organize ['ɔ:gənaɪz], organization [,ɔ:gənaɪ'zeɪʃən], lecture ['lekʧə], clinic ['klɪnɪk], control [kən'trəul], diagnostic [,daɪəg'nɔstɪk], provisor [prə′vaızə], academician [ə,kædə'mɪʃən], clinic ['klɪnɪk], doctor ['dɔktə], rector ['rektə], assistant [ə'sɪstənt], guide [gaɪd], analytical [әnә′lıtıkәl].
Exercise 3. Образуйте новые слова и переведите их.
1) The nouns by adding -er (-or): to train, to instruct, to teach, to work, to demonstrate, to read.
2) The adjectives by adding -al: industry, pharmacy, stomatology, education, experiment, practice clinic, medicine, analysis, recreation.
3) The families of the words: to arrange, arrangement; to teach, teacher; to instruct, instruction, instructor; to prepare, preparation, preparatory; stomatology, stomatological, stomatologist; medicine, medical, medicinal; to head, a head; to guide, a guide, guidance; to practise, practice, practical, practically; to educate, education, educational; skill, skillful, skillfully; science, scientific, scientist.
Exercise 4. Запомните следующие фразы и найдите их соответствия:
| 1. At the department of … 2. At the head of … 3. Is headed by … 4. Is assisted by … 5. Is awarded the Order … 6. The course of study … 7. In practical work … 8. To a great extent … | a) курс обучения; b) в практической работе; c) возглавляется; d) во главе; e) в значительной степени; f) на кафедре; g) награждается; h) помогает |
Exercise 5. Переведите следующие словосочетания:
Medical educational establishment; regional hospital; pharmaceutical education; to be awarded the Order of Peoples’ Friendship; day-time and correspondence department; to train the specialists in …; Public Health Service; to have a rich experience; a member of the Association of higher and continuous education; spacious lecture halls; well-equipped laboratory; scientific-research laboratory; educative-industrial pharmacy; theoretical knowledge and practical skills; highly-skilled teachers; the teaching staff; academic affairs, research and administrative work; teach, instruct and guide students; educational process; educational and scientific books.
Exercise 6. Изучите примеры, обратив внимание на употребление следующих глаголов:
To learn = to get knowledge of some subject or skill in some activity – учить, выучить.
He learns typing at school.
She learnt to read when she was 5.
You should learn the poem by heart.
To study = to gain knowledge, it refers only to knowledge, not skills or abilities – изучать, учиться.
He studies at Princeton.
BUT: He goes to school.
He is a first – year student.
He learns English at school.
To do/ to get on well = to be a bright student – хорошо учиться.
How is he getting on at school?
He is doing well at school.
To teach = to give a person knowledge, to give lessons – преподавать, обучать.
He teaches for a living.
Who teaches you English? = Who do you have for English?
To train = to give teaching and practice, usually for a particular job or skills – готовить, обучать, тренировать.
College of education trains 200 teachers a year.
She is a trained typist.
To instruct = to teach a practical skill.
Mr. Smith instructs them how to drive.
Education (general), training (more practical ), tuition (refers to costs) – обучение, подготовка.
Tuition fee is rather high.
Exercise 7. Заполните пропуски соответствующими глаголами:
1. Is he … well at school? 2. He … to high school. 3. He is a first … student. 4. The … is smaller at state universities. 5. They … girls to be pharmacists. 6. Higher … in US is rather expensive. 7. Mr. Bell … me how to ride a horse. 8. She went to France for a year to … French there. 9. Who do you … for physics? 10. When did you … to swim? 11. We … math every day. 12 He is a … driver. 13. You may get vocational … at special colleges. 14 The most famous professors … at Yale. 15. It’s very difficult to … and work at the same time.
Speech patterns
Interrogative patterns.
Mind that questions like that are not asked to get information but are used to express your reaction to what has been said. Such questions are called echo questions. In particular, they may show your interest, surprise, etc.
- Human nature is much the same everywhere.
- Is it?
* * * *
Young men are often obstinate
- Are they?
* * * *
- One should be prepared to take risks sometimes.
- Should he?
Respond to the statements.
1. You are almost half an hour late.
2. Mary may keep the book for seven days.
3. The only place to work in piece is the library.
4. Julia was absent from her last English class.
5. It is up to you to decide.
6. All of them were in a very nervous state.
7. There is something to talk about.
8. You will speak first.
Respond to the negative statements.
- I wouldn’t miss your party for the world.
- Wouldn’t you?
* * * *
- You can’t help it.
- Can’t I?
* * * *
- There is not any evidence.
- Isn’t there?
Mind contractions: isn’t (is not), aren’t (are not), wasn’t (was not), weren’t (were not), can’t (can not), couldn’t (could not), won’t (will not), shan’t (shall not), wouldn’t (would not), shouldn’t (should not), mightn’t (might not), mustn’t (must not), needn’t (need not).
1. The children were not in the room.
2. Their methods are not correct.
3. It’s not up to me to decide.
4. He wasn’t speaking for all of us.
5. Joe will not write any notes in textbooks.
6. You shall not make remarks tike those.
7. You must not interfere.
8. They needn’t worry.
9. I’m not very fond of staying in other people’s houses.
Exercise 1. Remember the pattern.
It takes me … minutes (hours, days, etc.) to do something.
Мне требуется … минут (часов, дней и т.п.) чтобы сделать что-то.
A. Translate the following sentences.
1. It takes me half an hour to cook dinner.
2. It took him long to translate this text.
3. How long will it take you to do this job?
4. It takes me an hour and a half to do our flat.
5. It took me twenty minutes to get to the place.
6. It will take us some hours to prepare everything for the test.
7. It takes me forty-five minutes to get to the university.
B. Answer the following questions using the pattern given above.
| How long How mach time | } | does it take you | to do your morning exercises? to prepare breakfast? to have breakfast (dinner, supper)? to get to your hostel (home, university)? to do your English homework? to look through newspapers? to speak over the phone with your friends (parents)? |
C. Ask your group mates about his (her) actions in the Past and Future. Use the following models:
| Did it take you long …? How long did it take you …? |
| Will it take you long …? How long will it take you …? |
Part II
Grammar practice
Table 1
Видо-временные формы английского глагола в действительном залоге
| Indefinite (Simple) Простое | Continuous (Progressive) Длительное | Perfect Завершенное | Perfect Continuous Завершенно-длительное | |
| Констатация факта to V | Процесс to be V-ing | Завершенность to have V3 | Процесс уже в течение некоторого периода времени to have been V-ing | |
| P R E S E N T | V, V-s I write Я пиш у (часто) |  am
is V-ing
are
I am writing
Я пишу (сейчас) am
is V-ing
are
I am writing
Я пишу (сейчас)
| 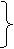 have
V3
has
I have written
Я написал (сегодня, уже, только что) have
V3
has
I have written
Я написал (сегодня, уже, только что)
| 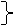 have been
has V-ing
I have been writing
Я пишу (уже час; с двух часов) have been
has V-ing
I have been writing
Я пишу (уже час; с двух часов)
|
| P A S T | V – ed, V2 I wrote Я (на)писал (вчера; два дня тому назад) |  was
V-ing
were
I was writing
Я писал (вчера в три часа; когда он вошел; пока он читал) was
V-ing
were
I was writing
Я писал (вчера в три часа; когда он вошел; пока он читал)
| had V3 I had written Я написал (вчера к трем часам; до того, как он пришел) | had been V-ing I had been writing Я писал (уже два часа, когда он пришел) |
| F U T U R E | shall/will V I shall/will (I’ll) write Я напишу, буду писать завтра. | shall/will be V-ing I shall/will (I’ll) be writing Я буду писать (завтра в 3 часа). | shall/will have V3 I shall/will (I’ll) have written Я напишу (завтра к трем часам; до того, как он придет). | shall/will have been V-ing I shall/will (I’ll) have been writing Я буду писать (завтра уже 3 часа, когда он придет). |
V – основа глагола;
V-ed = V2 – прошедшее простое время (Past Simple); вторая форма глагола;
V3 – причастие II (Participle II); третья форма глагола;
V-ing – причастие I (Participle I); четвертая форма глагола.
Exercise 1. Определите время, используя таблицу:
| 1. am V-ing 2. V-s 3. V 4. have V-ed (V3) 5. V-ed 6. will have V-ed (V3) | 7. had V-ed 8. was V-ing 9. will V 10. has V-ed 11. had been V-ing 12. has been V-ing | а) настоящее б) прошедшее в) будущее |
Exercise 2. Соотнесите формы глагола с их видовыми характеристиками.
| 1. to be V-ing 2. V-s, V 3. to have been V-ing 4. to have V-ed (V3) 5. will V 6. V-ed | а) констатация факта (Indefinite) б) завершенность действия (Perfect) в) процесс, незаконченность действия (Continuous) г) действие, совершенное уже в течение определенного периода времени (Perfect Continuous). |
Exercise 3. Прочтите предложения. Определите, какая характеристика действия заложена в каждом глаголе.
1. Я учу английский язык каждый день. 2. Я учу новые слова. Не мешай мне. 3. Я учил эти слова вчера. 4. Я выучил слова. Проверь меня. 5. Я буду учить слова завтра. 6. Я учил слова вчера, когда ты смотрел телевизор. 7. Я буду учить английский завтра в 6 часов вечера. 8. Вчера к 6 часам я уже выучил все слова. 9. Я надеюсь, что к 7 часам я их выучу. 10. Я изучаю английский уже 3 года. 11. Я учил слова уже час, когда пришла сестра. 12. На будущий год я буду изучать английский язык уже 5 лет.
Exercise 4. Пользуясь таблицей временных форм глагола, определите, какую видовую характеристику вы выбрали бы для перевода следующих предложений:
а) незаконченность (процесс)
б) завершенность (результат)
в) констатация факта (регулярность)
г) процесс + завершенность уже в течение определенного периода времени.
| 1. Я пишу | а) сейчас. б) уже 20 минут. в) каждый день. |
| 2. Я написал сочинение | а) уже (на этой неделе). б) вчера. в) вчера к 7 часам. |
| 3. Я писал статью | а) вчера. б) вчера, когда вы пришли. в) вчера уже 3 часа, когда вы пришли. |
| 4. Я напишу сочинение | а) завтра. б) завтра к 7 часам. |
| 5. Я буду писать сочинение | а) когда он придет. б) уже час, когда ты придешь. |
Exercise 5. Найдите сказуемое, определите его время и переведите, исходя из его характеристики.
1. I study at the Medical University. 2. I finished school last year. 3. I have just spoken to the dean. 4. I shall become a pharmacist in future. 5. I have just studied it. 6. I had studied this topic before he came. 7. He will have completed the work by Friday. 8. I have been working there for three months. 9. Before I entered the University I had been studying at school for 11 years. 10. Yesterday from 10 to 12 the students were listening to the lecture. 11. Don’t disturb me. I am preparing for my English lesson. 12. Students usually take exams twice a year, in January and in June. 13. By July I will have already passed the first-year exams. 14. If you come, we will go to the University. 15. I have something in my eye.
Exercise 6. Translate into English consulting the grammar of the lesson:
1. Я учусь в медицинском университете.
2. Я учусь в университете уже три месяца.
3. Сейчас я учу английскую грамматику.
4. К концу второго года я закончу обязательный (compulsory) курс английского языка.
5. До поступления в университет я учился в школе.
6. Я поступил на фармацевтический факультет.
7. Вчера с 7 до 10 вечера я учил химию.
| Grammar: | Word order in affirmative and interrogative sentences. |
Прямой порядок слов:
| Обстоятельство – Подлежащее – Сказуемое – Дополнение – Обстоятельство |
Обстоятельство может указывать время, место совершения действия, образ действия, причины, цели. Несколько обстоятельств в предложении располагаются в следующем порядке: образа действия (1), места (2), времени (3).
| He walks slowly (1). | Он ходит медленно. | |
| He arrived in London (2) yesterday (3). | Он приехал в Лондон вчера. | |
| The baby slept quietly (1) in his cot (2) all night (3). | Ребенок спокойно спал в своей кроватке всю ночь. |
Обстоятельство времени может находиться в начале предложения, обстоятельства, указывающие на частоту совершения действия (usually, frequently, often и т.д.), перед смысловым глаголом.
Вопросительные предложения могут быть в виде общего вопроса, специального вопроса, разделительного вопроса, альтернативного вопроса.
Общий вопрос задается, чтобы получить ответ «да» или «нет», начинается со вспомогательного или модального глагола.
| вспомогательный или модальный глагол | подлежащее + смысловой глагол сказуемого + дополнение + обстоятельство |
| Did you go to school yesterday? | Ты ходил в школу вчера? |
Специальный вопрос задается к определенному члену предложения. Он начинается с вопросительного слова (или группы слов).
Вопрос к подлежащему предполагает замену подлежащего вопросительными словами who или what, порядок слов не меняется.
| вопросительное слово + сказуемое + дополнение + обстоятельство |
| Who called up in the morning? | Кто звонил утром? |
Вопрос к другим членам предложения предполагает схему общего вопроса.
| вопросительное слово + вспомогательный или модальный глагол | подлежащее + сказуемое + дополнение и / или обстоятельство |
| What could I do then? | Что я мог сделать тогда? |
Вопросительные слова: Who (кто), What (что), Where (где), When (когда), Why (почему), How (как, каким образом), How well (насколько хорошо), How long (как долго), Which (который), How much/many (сколько).
Альтернативный вопрос предполагает выбор между двумя суждениями. Он строится как общий вопрос.
| Do you live in Moscow or in Kursk? | Вы живете в Москве или Курске? |
Разделительный вопрос соответствует русскому «не так ли?». Разделительный вопрос присоединяется к утвердительному или отрицательному повествовательному предложению, имеет вид краткого общего вопроса, включающего вспомогательный глагол, характерный для данного предложения, и местоимение, заменяющее подлежащее. Вспомогательный глагол имеет отрицательную форму, если предложение утвердительное, и утвердительную форму, если предложение отрицательное.
| He speaks a lot, doesn’t he? | Он много говорит, не так ли? | |
| He has not read this book, has he? | Он не прочитал эту книгу, не так ли? |
Exercise 1. Составьте предложения из следующих слов:
1. of, Medical, the, regional, on, basis, institute, was, hospital, organized, our.
2. began, 1941, War, in, Patriotic, the Great.
3. to, teachers, of, went, students, and, a lot, front, the.
4. university, foreign, trains, our, staff, for, medical, countries.
5. university, famous, are, talented, many, there, and, scientists, our, in.
6. work, scientific, in, part, active, an, take, students, the.
7. clinical, improved, the, University, has, and, considerably, base.
8. faculty, was, in 1959, founded, the, pharmaceutical.
Exercise 2. Составьте вопросы, изменив порядок слов в предложении:
1. Medical Institute was organized in 1934.
2. The teaching staff was not permanent at that time.
3. The pharmaceutical faculty is a real center of Belarusian pharmaceutical education.
4. In 1943 in Yaroslavl Medical Institute was restored with the joined staff of Minsk and Vitebsk.
5. Medical Institute has expanded during the post war period.
6. More than 1370 physicians and pharmacists have been trained at the Overseas Students Training faculty.
7. VMI was the first to receive the right of training medical staff for foreign countries.
8. VSMU has trained several thousands of specialists.
Exercise 3. Определите члены предложения и расположите их в таблице:
1. The head of the faculty is the Dean.
2. More than 7 thousand students study at these faculties.
3. The University pays attention to the practical skills of the students.
4. Pharmacists are trained at the Pharmaceutical department.
5. Before the Great Patriotic War 808 graduates got their diplomas.
6. There is a special scientific laboratory.
7. In 1946 the Institute resumed its work in Vitebsk.
Table
| группа подлежащего | группа сказуемого | группа дополнения | группа обстоятельства |
TIME FOR FUN
At the Top
“A telegram from George, dear.”
“Well, did he pass the examination this time?”
“No, but he is almost at the top of the list of those who failed. ”
* * * *
“ Did the play have a happy ending?”
“Yes, everybody was happy when it ended. ”
* * * *
Uncle Bob: Well, Frank, what are you going to do during this vacation?
Frank: Last year I had mumps (свинка) and chicken-pox (ветряная оспа). This year I don’t know what I am going to do.
* * * *
Doctor: What your husband needs, Mrs. Brown, is a complete rest. I have prescribed a sleeping pill.
Mrs. Brown: Very well, doctor. When shall I give it to him?
Doctor: Don’t give it to him. Take it yourself.
* * * *
“You were late this morning, Brown.”
“Yes, sir. I’m sorry. I overslept. ”
“Good gracious! Do you sleep at home as well?”
* * * *
He Must Go
Two men were going in a train. One of them asked the other:
“ Are you going to Brown’s lecture today?”
“Yes, I am,” said the other.
“Take my advice and don’t go,” said the first, “I hear he is a very bad lecturer.”
“I can’t help it,” said the other. “I must go, I’m Brown.”
* * * *
A Question to the Point
The professor was delivering the final lecture of the term. He put much emphasis on the fact that each student should devote all his time to preparing for the final examination. He said:
“The examination papers are now in the hands of a printer. Are there any questions?”
Silence prevailed. Suddenly a voice from the rear inquired:
“Who is the printer?”
* * * *
“What are you doing, Peter?”
“I’ m writing a letter.”
“And what were you doing ten minutes ago?”
“I was doing my lessons. And maybe you want to know what I shall be doing in twenty minutes, Alec?”
“Yes, Peter, what will you be doing?”
“I shall be beating you if you don’t stop asking me stupid questions.”
Part III
Reading Comprehension
Read and translate text 1.
Text 1
Our University
Vitebsk State Medical University is one of the most prestigious medical educational establishments in Belarus. This institution has been playing an important role in the development of medical science and training of medical and scientific personnel. Nowadays the University has 7 faculties: General Medicine Faculty, Pharmaceutical faculty, Stomatological Faculty, Overseas Students Training Faculty, Post-graduate Training Faculty, Faculty of Pedagogics and Psychology of Higher School, Preparatory Training Course. Physicians and surgeons are trained at the faculty of General Medicine, the faculty of Stomatology trains stomatologists or dentists. Pharmacists are trained at the faculty of Pharmacy at both day-time and correspondence department. The head of each faculty is the Dean. More than 7 thousand students study at these faculties. VSMU is headed by the Rector who is assisted by the Vice-Rectors responsible for academic affairs, research and administrative work. Educational process is organized at 60 departments. The head of the department, usually a professor or associate professor, is in charge of the work of the department. The teaching staff consists of doctors of sciences, candidates of sciences, instructors and laboratory assistants. Lectures are delivered by professors or associate professors, while instructors and laboratory assistants teach, instruct and guide students in their practical work. The students attend lectures, seminars, practical classes and scientific conferences. The students study in the spacious lecture halls, well-equipped laboratories, and modern computer classes. In its disposal, the University has 3 educational buildings, a scientific research laboratory, a dental clinic, an educational manufacturing pharmacy and a control analytical laboratory.
The University pays attention to providing the students with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The pharmacy students have an opportunity to study in the botanical garden and numerous chemists’. The medical and the stomatological students get practical skills in the majority of city clinics containing modern medical-diagnostic equipment.
VSMU has a rich experience in training students from different countries. Since 1981 the University has been effectively training the specialists in medicine and pharmacy for the needs of foreign Public Health Services. For the large merits in this work our University was awarded the Order of Peoples’ Friendship.
The University has become a member of the Association of higher and continuous medical and pharmaceutical education of medical institutions of higher learning of Russia.
At the University there is a perfect library, full of various editions. The majority of books are educational and scientific ones.
The University has 5 comfortable hostels. The students from other towns are given hostel accommodation. As to cultural and recreational activities at the University, they are quite various, and to a great extent are arranged by the students themselves. They participate in concerts, parties, discos, folk orchestras, in the choreographic ensemble, in the vocal music group, etc.
The students are supposed to master the fundamental subjects and to follow the traditions of the oldest Medical University.
Exercise 1. Look through the text and explain why:
1. Mostly the Simple Present Tenses are used
2. The Present Perfect Tense is used in one sentence.
Exercise 2. Find the synonyms:
| department, stomatologist, to deliver a lecture, pharmacist, institution, physician, experience, to guide, day-time student, to train. | pharmaceutist, faculty, to give a lecture, dentist, to supervise, full-time student, establishment, practical skills, general practitioner, to teach. |
Exercise 3. Make up word combinations:
| A.Educational manufacturing, control-analytical, educational, correspondent, skilled, medical-diagnostic, spacious, fundamental, recreational, research. | Work, laboratory, pharmacy, equipment, establishment, lecture halls, department, subjects, teachers, activities. |
| B.To organize, to train, to be responsible for, to guide, to follow, to be awarded, to pay attention, to be headed by, to deliver, to attend, to give. | Lectures, educational process, the traditions, the Dean, academic work, theoretical knowledge, students, the order, pharmacists, hostel accommodation, classes. |
Exercise 4. Match the names of faculties with their English equivalents.
| 1. Лечебный факультет | a) Post-graduate training faculty |
| 2. Фармацевтический факультет | b) Overseas students training faculty |
| 3. Стоматологический факультет | c) General medicine faculty |
| 4. Подготовительное отделение | d) Pharmaceutical faculty |
| 5. Факультет подготовки иностранных студентов | e) The faculty of pedagogics and psychology of higher school |
| 6. Факультет постдипломной подготовки | f) Stomatological faculty |
| 7. Факультет педагогики и психологии высшей школы | g) Preparatory training course |
Exercise 5. Agree or disagree with the following sentences using the formulas of agreement and disagreement:
Use: I quite agree with you; That’s right; I’m of the same opinion; I disagree; I differ from you.
1. Pharmacists are trained at the Stomatological faculty.
2. The Pharmaceutical faculty of VSMU is the center of Belarusian pharmaceutical education.
3. Assistants usually deliver lectures.
4. The Dean is responsible for administrative work.
5. The students have an opportunity to study in the botanical garden, in the majority of city clinics.
6. The Pharmaceutical faculty was organized in 1980.
7. There are 52 departments at the University.
8. Each department is headed by the professor or associate professor.
9. VSMU has a rich experience in teaching students from different countries.
Exercise 6. Put questions to the following statements.
1. VSMU was founded in November, 1934. (When?...)
2. There are 7 faculties at our University. (How many?...)
3. The faculty of General Medicine trains physicians. (What does?...)
4. Teachers, instructors, and laboratory assistants teach, instruct and guide students in their practical work. (What do?... In what?...)
5. For the large merits in training specialists for foreign Public Health Services the University was awarded the Order of Peoples’ Friendship. (Why?...)
6. Students study in the spacious lecture halls, well-equipped laboratories and modern computer classes. (Where do?...)
7. The University has 5 comfortable hostels. (How many?...)
8. The first- year students master the fundamental subjects. (What do?...)
Exercise 7. Say the following in English:
Практические навыки, развитие медицинской науки, готовить специалистов, возглавлять университет, быть ответственным за учебную работу, заведующий кафедрой, читать лекцию, обучать студентов, хорошо оборудованные лаборатории, современный компьютерный класс, преподавательский состав, теоретические знания, ботанический сад, эффективная подготовка специалистов, соблюдать традиции университета, комфортабельные общежития, большие заслуги, организовывать отдых, участвовать в концертах.
Exercise 8. Translate into English:
1. На лечебном факультете готовят врачей и хирургов.2. Наш вуз уделяет внимание, как теоретическим знаниям, так и практическим навыкам студентов. 3. Проректоры отвечают за учебную, научную и административную работу университета. 4. Преподавательский состав включает докторов наук, кандидатов наук, ассистентов и лаборантов. 5. Лекции читают профессора или доценты. 6. Студенты обучаются в просторных аудиториях и современных компьютерных классах. 7. Студенты фармацевтического факультета имеют возможность проходить практику в ботаническом саду и многочисленных аптеках. 8. С 1981 года университет готовит специалистов для зарубежных стран. 9. Иногородние студенты обеспечиваются общежитием. 10. Свой отдых, в большинстве случаев, студенты организуют сами. 11. Студенты должны овладевать фундаментальными науками и соблюдать традиции университета.
Exercise 9. Answer the questions on the text.
1. Can you tell the group mates about the faculties of your University?
2. Who heads the University, the faculty, the department?
3. What is the teaching staff of the University?
4. What are the facilities of studies at the University?
5. Does the University train specialists for different countries? If, yes, what are they?
6. Are all the university students given hostel accommodation?
7. Is it necessary to follow the traditions of the University? Why?