First Aid Steps
Many deaths and impact of injuries can be prevented with First Aid if causes are treated immediately.
First aid is the initial care given to an injured person. Mostly, this timely care prior to the arrival of the medical help means the difference between life and death.
It must start immediately when the injury or illness occurs and continue until medical help arrives or the casualty recovers.
The basic aims of first aid are:
- To save life
- To protect the casualty from getting more harm
- To reduce pain and Priorities of Casualty Treatment
Priorities of Casualty Treatment
- Asphyxia [æs’fɪksɪə]
- Cardiac Arrest
- Bleeding
- Other Injuries/Illnesses
- Shock
IMMEDIATE REQUIREMENT
Critical four minutes
One of the most common causes of a road accident death is due to loss of oxygen supply. This is mostly caused by a blocked airway. Normally it takes less than four minutes for a blocked airway to cause death.
The ‘golden hour’
The first hour after the trauma is called the ‘golden hour’. If proper first aid is given, road accident victims has a greater chance of survival and a reduction in the severity of their injuries.
Words
Impact – воздействие, влияние, удар
Prevent – предотвращать
Treat - лечить
Initial – начальный, исходный
Prior – предшествующий
Occur – происходить, иметь место
Casualty – жертва, потеря, несчастный случай, авария, раненый, убитый
Cardiac Arrest – остановка сердца
 Words
Words
Response – реакция, отклик
Lateral – латеральный, боковой, горизонтальный
Commence – начинать
Cardio pulmonary resuscitation – сердечно-легочная реанимация
Expired air resuscitation (ear) – легочная реанимация
AIRWAY
(Open and clear)
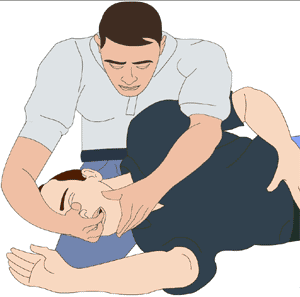 Check to see if the casualty's airway is clear. If not, examine and clear airway.
Check to see if the casualty's airway is clear. If not, examine and clear airway.
1. Support the casualty in the side position and tilt the head back and a little downward.
2. Open the mouth and clear foreign objects (e.g. broken teeth, food or vomit)
3. Place one hand high on the casualty's forehead to provide support
4. Support the chin with the other hand
5. Tilt the head backwards slightly
6. Lift the jaw and open the casualty's mouth slightly
Remember, there may be spinal injuries. Never roll an unconscious patient onto their back as their tongue may fall to the back of their throat and obstruct their airway.
Words
Tilt – наклонять
Downward – вниз
Unconscious – бессознательный
BREATHING
 Once the airway has been cleared, check if the casualty is breathing.
Once the airway has been cleared, check if the casualty is breathing.
1. Check for breathing. Look, feel and listen.
2. If the casualty is breathing, leave them in the Lateral (sideward) position.
3. Monitor and manage shock, bleeding and any other injuries
4. If the casualty is not breathing, support the head and neck, then roll onto their back and give 5 full breaths in 10 seconds.
EXPIRED AIR RESUSCITATION (EAR)
Start EAR if the causality is not breathing. EAR is also called mouth-to-mouth.
There are three methods of EAR:
- Mouth-to-mouth
- Mouth-to-nose
- Mouth-to-mask
Turn the casualty to his side to clear the airway before starting EAR
Mouth to Mouth
1. Turn the casualty onto his back
2. Tilt the head back slightly and lift the jaw forward.
3. Pinch the casualty’s nostrils with thumb and finger to seal the nose.
4. Take a deep breath and breathe into the casualty's mouth.
5. Remove lips. Allow chest to fall. Turn your head to the side to check if the chest is rising and falling after each inflation
6. If chest does not rise, check the angle of the head then check the airway. If the stomach rises, decrease the amount of breath.
7. Give 5 full breaths in 10 seconds, then check the carotid (neck) pulse
8. If pulse is present, commence EAR at the rate of 15 breaths per minute.
Mouth to Nose
This is done if there is an injury in the mouth
1. Tilt the casualty's head back
2. Close the casualty's mouth.
3. Take a deep breath and breathe into the casualty's nose.
4. Take your mouth away and open the casualty's mouth
5. Give 5 full breaths in 10 seconds
6. Check the carotid (neck) pulse. If pulse is present, commence EAR at the rate of 15 breaths per minute.
Words
Pinch – ущипнуть, зажать
Seal - опечатать
Inflation – надувание, вздутие
Decrease - уменьшать
Amount – количество
CIRCULATION
Check if the casualty has a pulse.
If casualty has a pulse but is not breathing, start EAR at 15 breaths per minute.
If no pulse is present immediately start CPR.
How to check pulse?
Feel for a carotid (neck) pulse by placing the pads of your fingers in the groove beside the Adam's apple or the middle of the neck on a woman. You can check on either side of the neck. You must check the pulse for 10 seconds.
Note: When the body is in shock, it often shuts down the peripheral circulation, including the radial (wrist) pulse. Therefore it is not advised to check radial pulse.