Unit 5. Internal organs
Human body is known as organism. Human body consists of various organ systems. Each organ system performs a particular task.
Appendix
It is a blind-ended tube that is connected to the cecum. The appendix is located near the junction of the small and large intestines.
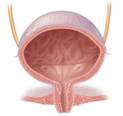
Bladder
In this organ, the urine that is filtered from the kidneys is collected before being disposed off by urination. The bladder is a muscular organ that is elastic in nature. It is located on the pelvic floor.
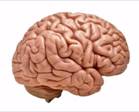
Brain
It is the most important organ of the human body, and it controls all the other parts. It is the center of the nervous system, and is the most complex of all internal organs. The brain controls our sense of vision, hearing, taste, smell, balance, and feeling.
Esophagus
It is a long muscular tube that passes from the pharynx into the stomach. This organ connects the mouth to the stomach, and is about 25 to 30 cm long.
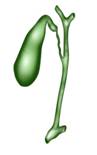
Gallbladder
It is one of the smallest internal organs of the human body. It helps in the process of digestion. It is located in the concave portion of liver that is called the gallbladder fossa. The length of this portion is about 8 cm in adults.
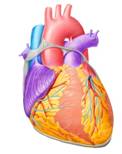
Heart
After the brain, the heart is the second most important internal organ in humans. It is a muscular organ whose main function is to pump oxygenated blood throughout the body through blood vessels. This action is carried out by repeated and rhythmic contractions. On an average, the human heart beats about 72 times per minute, and weighs 250 to 300 gm in females, and 300 to 350 gm in males.
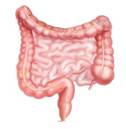
Intestines
They are a segment of the alimentary canal, and they extend from the stomach to the anus. They are divided into: small intestine and the large intestine.
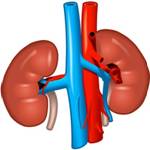
Kidneys
They serve as the most important part of the urinary system. Their function is regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid-base balance, regulation of blood pressure, production of urine, etc.
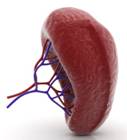
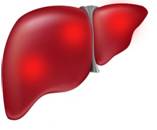
Liver
It is one of the most vital internal organs of the human body. The liver is an absolute necessity for survival. It carries out several functions including detoxification of blood, production of biochemicals for digestion, and protein synthesis.
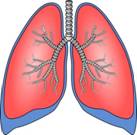
Lungs
These organs are responsible for respiration. In humans, a pair of lungs is located in the chest on either side of the heart. Their function is to transport atmospheric oxygen into bloodstream, and release carbon dioxide from blood into the atmosphere.
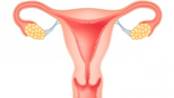
Ovaries
They are ovum-producing reproductive organs that are present in pairs in females. They are located in the lateral wall of the pelvis.
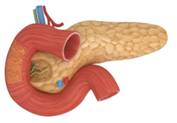
Pancreas
They belong to both the endocrine and digestive systems. These organs produce important hormones like insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. They also produce pancreatic juice that contains digestive enzymes. If the pancreas do not function normally, it may lead to diabetes mellitus.
Spleen
The organ is very important with respect to the immune system. It is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. Its function is to remove old red blood cells and also to recycle iron. The spleen in an adult human body is about 11 cm in length.
|
|
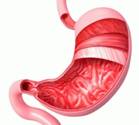
Stomach
The muscular, hollow bag in the alimentary canal is called the stomach. It is the primary organ of the digestive system that is involved in the second phase of food digestion. The location of this organ is between the esophagus and small intestine.
Thyroid gland
The largest endocrine gland of the human body is the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck. It helps to control the use of energy in the body.
Uterus
It is the most important part of the female reproductive system. This organ is internally connected to the fallopian tubes on each side, and opens into the vagina at one end. In this organ the fetus develops during gestational period.
Word-box
| bladder – мочевой пузырь brain – мозг esophagus – пищевод gallbladder – желчный пузырь heart – сердце intestines – кишечник kidneys – почки liver – печень lungs – лёгкие ovaries – яичники pancreas – поджелудочная железа spleen – селезенка stomach – желудок thyroid gland – щитовидная железа uterus – матка alimentary – пищеварительный cecum – слепая кишка junction – соединение urine – моча | pelvic floor – диафрагма таза pharynx – глотка digestion – пищеварение concave portion – вогнутая часть fossa – впадина to pump – качать blood vessels – кровеносные сосуды rhythmic contractions- ритмичные сокращения urinary system – мочеполовая система electrolytes – электролиты acid-base balance – кислотный баланс detoxification – детоксикация bloodstream – кровоток ovum – яйцеклетка lateral wall of the pelvis – боковая стенка таза to recycle iron – перерабатывать железо fallopian tubes – маточные трубы gestational period – гестационный период (период беременности) |
Упр 1. Определите название внутреннего органа по картинке.
| 
| 
|
| 
| 
|
| 
| 
|
| 
| 
|