REPORT
On laboratory work №5
On the discipline “Electric machines”
Theme: “Research of the asynchronous machine in the mode of the asynchronous generator”
Specialty: 5B071800- Electrical Power Engineering
Done by: Shaimuradov E. Group: EPEe-15-10
Checked by: Abdullaev Z.M.
_________ ___________ “___” __________ 2017
(score) (signature)
Laboratory work № 5.Research of the asynchronous machine in the regime of the asynchronous generator
Objective of work: research of the method of switching on an asynchronous machine for operation in the generator mode. Investigation of the working properties of an asynchronous generator.
Program of work
1. To study the scheme for experimental research of asynchronous
generator.
2. Perform a test run of an induction motor and an engine
direct current.
3. Investigate an asynchronous motor in the asynchronous generator mode.
4. Conduct experimental data processing, compile a report and
draw a conclusion on work.
Explanations for work
In the laboratory work the following modules are used:
- Stand Power Module (SPM);
- power module (PM);
- Thyristor converter (TC);
- power module (PM);
- Measuring module (MM).
Before conducting laboratory work, you must bring the modules to their original state:
- the "Network" button of the TP module is set to the lower position, switch SA6 set to the lower position. Transfer the TP to the torque control mode (Appendix E);
- the investigated asynchronous machine is a part of the electric machine
The unit, which includes the M1 generator itself, the drive motor-a DC machine-M2 and a pulse speed sensor M3.
The circuit for removing the operating characteristics of an asynchronous generator is shown in Fig. 1.

Figure 1— Scheme for removing the performance of an asynchronous generator
The DC motor is connected to a thyristor converter. The anchor circuit is connected to the outputs of the regulated voltage source Umn, the excitation winding is connected to the outputs Uov.
The value of the speed n is observed on the power module indicator. Values of anchor current IH, armature voltage UN observe neither the TP indicator, stator current IF and stator voltage Uph are measured by the MI module.
1. Removing Performance
Performance characteristics are the power dependence,
which is supplied to the asynchronous generator P1, the phase current Iph, efficiency , slip s from the total active power P2 given by the asynchronous generator to the network: IF, P1, s, η, cosφ1 = f (P2).
The experiment is carried out in the following sequence:
- turn on the QF1 and QF2 automata of the MPS and MP modules, respectively,
the induction motor will start;
- Switch on the "Network" button of the TP - the voltage is applied to the thyristor
converter;
- apply for the operation of the TP (SA6) and select the direction of rotation
(SA5);
- By setting the torque potentiometer RP1 of the TP module, to monitor the speed of the unit. If it decreases, change the direction of the torque command;
- increasing the setting of the TP moment, change the speed of the unit. When
It is necessary to monitor the current of the armature of the DPT. He should not
exceed 1.5A.
The data of the experiment are listed in Table. 1, Table. 2.
Table 1 - Results of the experiment
| From the side of the asynchronous generator | |||||||
| Experiencedata | Calculationdata | ||||||
| Uф | Iф | n | P2 | cos 
| s | 
| 
|
| V | А | rpm | W | rad/s | % | ||
| 1,26 1,26 1,28 1,32 1,35 1,39 1,42 | -143,765 -121,7305 -74,3288 -48,1088 1,4641 17,2403 47,2452 | -0.049 -0.023 0.035 0.072 0.135 0.160 0.2 | 0.0087 -0.02 -0.031 -0.041 -0.05 -0.063 | 155,64 160,14 163,5 | 340,097 601,5155 247,268 77,335 1,26 12,46 27,28 |
Table 2 - Results of the experiment
| Onthe DC side | ||||||
| Experiencedata | Calculationdata | |||||
| Uя | Iя | Мэм | Iя0 | М0 | М1 | Р1 |
| V | А | Nm | А | Nm | Nm | W |
| 0,11 0,35 0,5 0,7 0,8 | 0,1463 0,462 0,6585 0,9205 1,048 1,31 | 0,2058 0,2069 0,2078 0,2084 0,2089 0,2094 0,21 | 0,2716 0,2752 0,2743 0,2745 0,2747 0,2743 0,273 | -0,2716 -0,1289 0,1877 0,384 0,7116 0,8386 1,037 | -42,2718 -20,2373 30,06 62,208 116,3466 138,37 173,18 |
After the end of the experiment, all the module switches are set to the initial state.
Estimated data.
Electromagnetic moment produced by a DC motor, N * m
МЭМ=СМ*IЯ,
where CM - is taken from the calibration curve, Sm = f (ω) (Appendix B).
The moment of idling of the DC motor, N * m
М0=СМ*IЯ0,
IЯ0 – no-load current; is taken from the calibration curve of the DC machine (Appendix B).
Useful torque on the DC motor shaft, Н*м
М1=МЭМ–М0;
The power supplied to the asynchronous generator from the DC motor is determined from the calculated data of this motor:

Losses in the stator winding, Wt
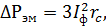
where rс – Stator winding resistance (Appendix B).
The total active power supplied by the asynchronous generator to the AC network, Wt:
Р2=P1–  PМЕХ.АД–
PМЕХ.АД–  РЭМ,
РЭМ,
where  PМЕХ.АД – mechanical losses of an asynchronous machine (Appendix B), Wt.
PМЕХ.АД – mechanical losses of an asynchronous machine (Appendix B), Wt.
Asynchronousgeneratorpowerfactor

Slip ofasynchronousgenerator

where n0 – synchronous speed, rpm.
The efficiency of an asynchronous generator, %

Based on the calculated data, construct the performance characteristics of an asynchronous generator: Р1, IФ, сosφ,  , s=f(Р2) at Uф=constand f=const.
, s=f(Р2) at Uф=constand f=const.

Figure 2— Operation characteristics of asynchronous generator
Conclusion: In this laboratory work was considered the asynchronous motor in the generator mode. The result of the laboratory work is shown in figure 2. From here we can see the operation characteristics of asynchronous generator. Then it would be concluded that asynchronous motor starts to work as the generator only when we rotate it at speed higher than speed of stator field rotation and the applied external power must be more than the losses in asynchronous motor.
Listofreferences
1 Копылов И.П. Электрические машины.-М.: Высшая школа, Логос, 2000. -607 с.
2 Брускин Д.Э., Зорохович А.Е., Хвостов В.С. Электрические машины. Ч. 1,2. -М.: Высшая школа, 1987.
3 Копылов И.П. Электрические машины.-М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1986.-360 с.
4 Вольдек А.И. Электрические машины.-Л.: Энергия, 1978.-832 с.
5 Костенко М.П., Пиотровский Л.М. Электрические машины. Ч.2 Машины переменного тока.- Л.: Энергия, 1973. - 412 с.