| 5 March (5th March) | the fifth of March / March the fifth |
| nineteen hundred and seven / nineteen oh seven |
Fractions and decimals
 a half a half
|  an eighth an eighth
|
 a third a third
|  three-eighteenths / three over eighteen three-eighteenths / three over eighteen
|
 two-thirds two-thirds
|  three over one six five three over one six five
|
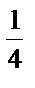 a quarter a quarter
| 0.3 (nought) point three |
 one and three-quarters one and three-quarters
| 6.07 six point oh seven |
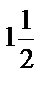 one and a half one and a half
| 10.75 ten point seven five |
Percentages
| 35 % | thirty-five per cent |
Temperature
| 24°C or F –10° | twenty four degrees centigrade / celsius or fahrenheit [ˊfærǝnhaɪt] ten degrees below zero / minus ten degrees |
Formulae reading
Basic formulae
1. Do you know how these formulae are spoken?

|

|

| 
|
Notice the signs which are used to indicate mathematical processes. Copy this into your notebooks.
| signs | spoken | noun / verb |
| + | plus [plʌs] | addition / add |
| – | minus [ˊmaɪnǝs] | subtraction / subtract |

| multiplied by / times | multiplication / multiply |
| : | divided by / over | division / divide |
2. Memorise how the above formulae should be spoken.
a plus b equals c
a minus b equals d
a times b equals e / a multiplied by b equals e
a over b equals f / a divided by b equals f
3. More mathematical symbols to memorise.
These signs () are called brackets.
These signs [ ] are called square brackets.
ABC are capital letters. 
abс are small letters.
Ax is read A subscript x
ā is read a barred [ba:d]
4. Practise reading these formulae aloud.

| a minus b in brackets times a plus b in brackets equals y |

| a open brackets 8 minus b close brackets equals x |

| 12 plus a minus b in brackets all over 7 a equals b |

| x open square brackets a minus b in brackets times a plus b in brackets minus 7 close square brackets equals nought [nɔ:t] |
5. Produce and recognise spoken forms of these simple formulae. Mind that the capital / small letter distinction is usually only made when both forms are used in the same equation.
1) 
|
6) 
|
2) 
| 7) 
|
3) 
| 8) 
|
4) 
| 9) 
|
5) 
| 10) 
|
6. Mind the full spoken version of these values. Practise reading them.

| x squared |
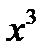
| x cubed |

| x to the power (of) n / x to the n |

| x to the power (of) n minus 1 / x to the n minus one |

| x to the power (of) minus n / x to the minus n |

| square root of x |
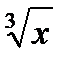
| cube root of x |

| n th root of x |
7. Write down the full spoken version of the following expressions. Read them out.
1) 
| 6) 
|
2) 
| 7) 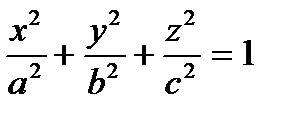
|
3) 
| 8) 
|
4) 
| 9) 
|
5) 
|
10) 
|
More complex formulae
1. Study the following table and read the examples aloud.
| symbol | meaning | example | spoken |
| º | equivalent to | xºy | x is equivalent to y |
| ¹ | not equal to | x¹y | x is not equal to y |

| approximately equal to | x  y y
| x is approximately equal to y |

| tends to | x 
| x tends to nought |
| < | less than | x<5 | x is less than five |
| > | greater than | x>5 | x is greater than five |
| << | much less than | y<<5 | y is much less than five |
| >> | much greater than | y >>5 | y is much greater than five |
| ≤ | less than or equal to | x ≤10 | x is less than or equal to 10 |
| ≥ | greater than or equal to | y ≥10 | y is greater than or equal to 10 |
| ∞ | infinity | x→∞ | x tends to infinity |

| proportional to |
x  y y
| x is proportional to y |
| ± | plus or minus | x=±2 | x equals plus or minus 2 |
| / | per | km/hr | kilometres per hour |
2. Here is the Greek alphabet. Make sure you know how this is read.
| Capital / small | Name | |
| Aα | alpha | [ˊælfǝ] |
| Bβ | beta | [ˊbi:tǝ; US: beɪtǝ] |
| Γγ | gamma | [ˊgæmǝ] |
| Δδ | delta | [ˊdeltǝ] |
| Εε | epsilon | [epˊsaɪlǝn; US: ˊepsɪlɔn] |
| Ζζ | zeta | [ˊzi:tǝ; US: ˊzeɪtǝ] |
| Ηη | eta | [ˊi:tǝ; US: ˊeɪtǝ] |
| Θθ | theta | [ˊθi:tǝ; US: ˊθeɪtǝ] |
| Ιι | iota | [aɪˊoutǝ] |
| Κκ | kappa | [ˊkæpǝ] |
| Λλ | lambda | [ˊlæmdǝ] |
| Μμ | mu | [mju:] |
| Νν | nu | [nju:; US: nu:] |
| Ξξ | xi | [ksaɪ] |
| Οο | omicron | [ouˊmaɪkrǝn; US: ˊɔmɪkrɔn] |
| Ππ | pi | [paɪ] |
| Ρρ | rho | [rou] |
| Σσ | sigma | [ˊsɪgmǝ] |
| Ττ | tau | [tau] |
| Υυ | upsilon | [ju:pˊsaɪlǝn; US: ˊju:psɪlɔn] |
| Φφ | phi | [faɪ] |
| Χχ | chi | [kaɪ] |
| Ψψ | psi | [psaɪ] |
| Ωω | omega | [ˊoumɪgǝ; US: ouˊmegǝ] |
3. Practise reading out these expressions.
1) 
| f equals one over two pi times the square root of LC |
2) 
| E equals sigmaT to the power of four |
3) 
| Capital W subscript s equals two pi small f over capital P |
4) 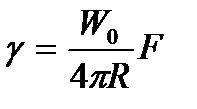
| Gamma equals W subscript oh over four piR all times F |
5) 
| Mu subscript oh equals four pi times ten to the power of minus seven capital H small m to the power of minus one |
6) 
| C equals L over R squared plus omega squared L squared |
7) 
| v subscript two equals the square root of open brackets, two e over m times capital V subscript two, close brackets |
8) 
| u equals a half sigma subscript upsilon squared all over K |
9) 
| sigma equals capital M small y small c all over capital I, plus capital P over capital A |
10) 
| gamma equals four Q over three piR squared times, open brackets, R squared minus gamma squared, close brackets |
4. Write down the following formulae in your notebooks. Check the results as a class.
1) V over I equals R (all capital letters)
2) P subscript one V subscript one equals P subscript two V subscript two (all capital letters)
3) one over u plus one over v equals one over f (all small letters)
4) capital F equals small m small v squared all over small r
5) one over R equals M over EI (all capital letters)
6) sigma over capital Y small n equals capital M over capital A small h capital R subscript small f
7) capital A equals two pi capital R subscript small c, open square brackets capital R subscript small c minus square root open brackets capital R subscript small c squared minus small d squared over four, close brackets, close square brackets
8) tau equals four capital Q over three pi capital R to the power of four, open brackets, capital R squared minus gamma squared, close brackets
9) F is proportional to M subscript one M subscript two all over R squared (all letters capital)
10) T squared over R cubed equals four pi squared over GM (all capital letters)