1. We use the Present Indefinite to express repeated actions in the present or permanent actions in the present.
E.g.: I sometimes play the piano three hours a day (a repeated action).
He lives in St.-Petersburg (a permanent action).
2. We use the Present Indefinite to express actions going on at the moment of speaking instead of the Present Continuous with stative verbs (to see, to hear, to know, to understand, etc.).
E.g.: I don’t understand what you mean.
I see a ship in the distance.
3. We use the Present Indefinite to express future actions in subordinate clauses of time, condition and concession and in clauses after the combinations “to see to”, “to take care”, “to make sure”.
a) We use the Present Indefinite to express future actions in subordinate clauses of time (в придаточных предложениях времени).
 E.g.: He will do it when you come.
E.g.: He will do it when you come.
main clause subordinate clause
when?
!!! Термином «clause» обозначается часть сложного предложения, которая содержит подлежащее и сказуемое. Внутри сложноподчинённого предложения есть два типа «clause»: главное предложение (main clause) и придаточное предложение (subordinate clause). Придаточное предложение зависит от главного, так как к нему можно задать вопрос от главного предложения. В вышеприведённом примере главное предложение (main clause) – это «He will do it». Зависящая от него часть, к которой мы можем задать вопрос, – это «when you come». «When you come» – это придаточное предложение (subordinate clause).
От того, какой вопрос мы задаём, зависит тип придаточного предложения (type of a subordinate clause). Если это вопрос «когда» (а также «до каких пор», как долго», и т.д.), то мы имеем дело с придаточным предложением времени (a subordinate clause of time). В вышеприведённом примере мы спрашиваем «Когда он это сделает?» и отвечаем «когда ты придёшь». Поэтому «when you come» – это придаточное предложение времени (a subordinate clause of time).
Subordinate clauses of time begin with the conjunctions “when”, “while”, “till / until”, “before”, “after”, “as soon as”, etc.
| Conjunction | Meaning | Example |
| when | when |  I shall speak to him when he comes. I shall speak to him when he comes.
 a subordinate clause of time
a subordinate clause of time
|
| as soon as | immediately after |   He will do it as soon as they come.
a subordinate clause of time He will do it as soon as they come.
a subordinate clause of time
|
| before | earlier than |   He will do it before you come.
a subordinate clause of time He will do it before you come.
a subordinate clause of time
|
| after | after |   He will do it after you come.
a subordinate clause of time He will do it after you come.
a subordinate clause of time
|
| till / until | up to the time that |   We shall stay here until he returns.
a subordinate clause of time We shall stay here until he returns.
a subordinate clause of time
|
| while | during the time that |   They will do it while you are here.
a subordinate clause of time They will do it while you are here.
a subordinate clause of time
|
Note: The conjunction “when” can introduce not only subordinate clauses of time but also object clauses (придаточные предложения, выступающие в функции дополнения). Object clauses answer the question “what”. We use the Future Indefinite in object clauses.
E.g.: what?
 I don’t know when he will come.
I don’t know when he will come.
 object clause
object clause
!!! Важно запомнить, что при выражении действия, относящегося к будущему, в придаточных предложениях времени (clauses of time) используется настоящее время, а в придаточных предложениях, выступающих в функции дополнения (object clauses), используется будущее время.
b) We use the Present Indefinite to express future actions in subordinate clauses of condition (в придаточных предложениях условия).
E.g.: on what condition?
 I shall ask him about it if he comes.
I shall ask him about it if he comes.
a subordinate clause of condition
Subordinate clauses of condition begin with the conjunctions “if”, “unless”, “on condition that”, “provided”, “in case”, etc.
| Conjunction | Meaning | Example | |||
| in case | because it is possible that something might happen |   Take an umbrella in case it rains.
a subordinate clause of condition Take an umbrella in case it rains.
a subordinate clause of condition
| |||
| unless | except if |   We shall go for a walk unless it rains.
a subordinate clause of condition We shall go for a walk unless it rains.
a subordinate clause of condition
| |||
| provided / providing (that) | but only if | He will give you his dictionary
  provided you return it tomorrow.
a subordinate clause of condition provided you return it tomorrow.
a subordinate clause of condition
| |||
| on condition that | but only if |  I will agree on condition that Mary teaches us. I will agree on condition that Mary teaches us.
a subordinate clause of condition |
Note: The conjunction “if” can introduce not only subordinate clauses of condition but also object clauses (придаточные предложения, выступающие в функции дополнения). Object clauses answer the question “what”. We use the Future Indefinite in object clauses.
E.g.: what?
 I don’t know if he will come.
I don’t know if he will come.
 object clause
object clause
!!! Важно запомнить, что при выражении действия, относящегося к будущему, в придаточных предложениях условия (clauses of condition) используется настоящее время, а в придаточных предложениях, выступающих в функции дополнения (object clauses), используется будущее время.
c) We use the Present Indefinite to express future actions in subordinate clauses of concession (в придаточных предложениях уступки)
Subordinate clauses of concession begin with the conjunctions “even if”, “even though”, “no matter how”, “however”, “whatever”, “whenever”, “wherever”, “whichever”, “whoever”.

E.g.: Even if he hates me, I shall tell him about it.
 |
a subordinate clause of concession

Whatever happens, he will come.
a subordinate clause of concession
 Come whenever you want.
Come whenever you want.
 |
a subordinate clause of concession
 Wherever you go, she will be with you.
Wherever you go, she will be with you.

a subordinate clause of concession

Whoever comes, don’t let him in.
a subordinate clause of concession
 Whichever toy you choose, you may take it.
Whichever toy you choose, you may take it.
a subordinate clause of concession
d) We use the Present Indefinite to express future actions in clauses after the combinations “to see to”, “to take care”, “to make sure”.
main clause 
 subordinate clause
subordinate clause
 E.g.: Make sure that you lock the door.
E.g.: Make sure that you lock the door.
Present Indefinite
!!! В главном предложении стоит «make sure», поэтому глагол в придаточном предложении ставится в настоящее время.
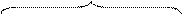
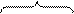 main clause subordinate clause
main clause subordinate clause
 E.g.: See to it that he does everything. (= See that he does everything).
E.g.: See to it that he does everything. (= See that he does everything).
Present Indefinite
!!! В главном предложении стоит «see to», поэтому глагол в придаточном предложении ставится в настоящее время.
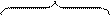 main clause
main clause 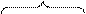 subordinate clause
subordinate clause
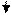 E.g.: Take care that they come.
E.g.: Take care that they come.
Present Indefinite
!!! В главном предложении стоит «take care», поэтому глагол в придаточном предложении ставится в настоящее время.
4. We use the Present Indefinite to express future actions which will take place according to a timetable, a schedule or an arrangement.
E.g.: The ship sails tomorrow.
5. We use the Present Indefinite to express past actions. We call it “the historic present” or “the dramatic present”.
E.g.: This morning I wake up and then, can you imagine, I see my cat with a mouse!
6. We use the Present Indefinite to express universal truths.
E.g.: The sun rises in the East.