The method of "center of gravity" is used for placement of selected new facilities.
It takes into account the location of existing facilities, the distance between the volumes of goods transported. The method is often used for placing intermediate storage facilities for semi-finished produce = промежуточных складов хранения полуфабрикатов or central distribution warehouses. In simplified form, this method assumes that all transport costs in forward and reverse direction are the same, and does not account for losses at case of partial load transport.
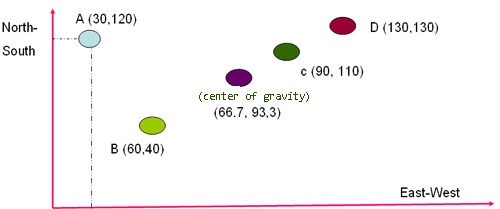
According to the method of "center of gravity" location of existing facilities are marked on the grid. The choice of the coordinate system is quite arbitrary=произвольный, случайный. The aim is to establish the relative distances between locations of objects. When making international decisions latitude and longitude coordinates are used.
Центр тяжести находят с помощью вычисления координат X и Y, что приводит к минимизации транспортных затрат. При этом используют такие формулы:
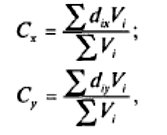
Сх — X coordinate of the center of gravity;
Су — Y coordinate of the center of gravity;;
dix — X c oordinate of place i;
diy- — Y c oordinate of place i;
Vi; — volume of goods transported to or from place i.
Example 1.
A department store has branches in four locations: A, B, C and D. Department Store has a Ware House at D and plans to seek the central location of the new house ware. Previously, it has been determined in advance the coordinates of 0.0. Store locations in A (30.120); D (130, 130), C (90, 110) and B (60.40). Total demand for containers every month for A (2000); D (1000), C (1000) and B (2000). Location A has coordinates d (1, x) = 30, d (1, y) = 120, and W1 = 2000. By using equations Center of gravity is obtained the desired central location.

REMINDER Process Flow Structure
Process Flow Structure defines type of material flow within working places.
Reseachers of this issue Robert Hayes and Steven Wheelwright define 4 main types of process flows.
Job Shop - This production of a wide range of different products in small parties which often requires different set and sequence of technological operations. Examples of such production can serve as commercial printing firms, companies working in aircraft manufacturing, metal and wood workshops (=мастерские), and factories producing printed circuit boards =печатные платы to order.
Batch – In fact, the company working on this principle produces the periodic order. This type of production is usually chosen, if a company has a relatively stable range of different products, each produced on a periodic basis - either by customer request or for the replenishment of stocks of the company. Most of the products are produced using the same technological scheme. As an example, the production of heavy equipment, electronic appliances and fine chemicals for organic synthesis = химических продуктов тонкого органического синтеза.
|
|
Assembly Line – Production of selected items that are automatically moved from one job to another with a controlled speed and in the sequence required for output. Examples are handmade toys and electrical appliances or automatic assembly of printed circuit boards.
Continuous Flow – Processing or further processing of indivisible materials such as oil, chemicals or beer. Like on an assembly line, production process takes place in a certain sequence, but in this case, the production flow is continuous. Such technologies are typically characterized by a high level of automation and, in fact, represent one integrated "car", which works 24 hours to avoid costly stops and starts.