But my take on KPIs is this.
1. Don’t have too many! I’ve literally seen KPI ‘packs’ the size of phone books, and even KPI sets circulated as a monthly magazine… that no one reads.
2. Make sure they ‘tie’ in with your goals and objectives. Do they directly support those objectives?
All you need to know about Supply Chain KPIs is right here
So that unfortunately means, that many of your supply chain KPIs may not be stock standard ones. But in Supply Chain you would normally expect to see this standard set, along with those that are more specific to your business needs.
· DIF – Delivery in Full
· DOT – Delivery on Time
· DIFOT – Delivery In Full on Time
· Cost as a percentage of sales (Logistics or Supply Chain)
· Inventory stock turns in Days.
KPIs in Supply Chain – The Basics
Overview
As in any business activity, supply chain operations need to focus constantly on improvement to compete in the market place. But how do you know if your supply chain performance is being maintained, or if it’s getting better, or worse?
What’s a KPI, Anyway?
KPI stands for Key Performance Indicator, and can be defined as a practical and objective measurement of progress, either:
· Towards a predetermined goal, or
· Against a required standard of performance
It might help to think of a KPI as something like an instrument on a car dashboard. Take a speedometer for example. If you are driving your car and you wish to maintain a speed of 50 KPH, you will use your speedometer to maintain that speed. You will drive a little faster if your speedometer needle drops below 50KPH or you will slow down if it climbs above the required speed.
You will use a KPI in the same way as your car’s speedometer. The only difference is that in most cases, you won’t wish to lower performance when a business activity exceeds the required standard. In fact, if your car has a fuel consumption gauge and you use this to try and drive economically, then you are making use of a bona fide KPI.
Why Are KPIs Important?
Using KPIs for performance measurement ensures that you are always evaluating your business activity against a static benchmark. This means that fluctuations are immediately visible and if performance moves in the wrong direction, action can quickly be taken to address the situation.
When a KPI shows that performance is consistently meeting or exceeding the required level, you can decide to raise the bar and set a higher standard to aspire to. For this reason, KPIs are essential for any business improvement strategy.
Apart from an internal desire to improve and compete, KPIs are likely to play a part in attracting and retaining customers. This is especially true in any business where customers tie into agreements or contracts. Service level agreements in particular will be monitored through KPIs agreed between a business and its customer, with the probability of penalties being applied when performance falls below agreed levels.
In short, KPIs provide visibility of business performance and allow objective quantitative and qualitative evaluation. When aligned with business goals, KPIs take away the guess work and enable focus to be centred on progress towards the goals.
Supply Chain KPIs
When measuring the effectiveness and cost of your supply chain you will need to set up and monitor KPIs which give visibility of cross functional activity as well as those which apply to individual supply chain components. Later in this e-Class we’ll look at some examples of functional and cross functional KPIs. Broadly speaking though, the following areas are those where KPIs will be necessary:
1. Order capture
2. Inventory management
3. Purchasing and supplier management
4. Production/manufacturing
5. Warehousing
6. Transportation
Cross functional KPIs are likely to provide snapshots of the following end to end performance factors:
· Perfect order (the degree of accuracy to which customers’ requirements are being met)
· Inventory levels
· Stock losses and/or damages
· Gross profit
· Cost of goods sold
· Total logistics cost
Cross functional KPIs should be constructed in such a way that each function can see its contribution towards the overall supply chain performance.
Main "plus" of this system determine the efficiency and effectiveness of the professional activity of heads of executive bodies are: Differentiation of performance of professional activities of persons holding public office, on the model and industry.repeated failure of sectoral indicators entails demotion or dismissal, the achievement of indicators leads to the conclusion that the head deserves encouragement. Failure of standard indicators suggests an inability to organize the work of the head of subordinates.accounting performance indicators executive authority in the evaluation of individual performance of the head of the authority. Analysis of the feasibility of a system of measuring the effectiveness of the heads of executive positions with the measurability of rationality and efficiency.forming performance and effectiveness without absolutism - the impossibility of making mistakes. Analysis of the causes of deviations from the established indicators, followed by timely introduction of the required changes and their implementation.
KPI: the lack of results in the United States
In the 1950s, a well-known management theorist Peter Drucker (Peter Drucker) laid down the concept of KPI.for the Americans at the time, taking into account the peculiarities of their mentality, it was some progress in improving productivity.
However, in the 1970s, Japanese companies began to open its production subsidiaries in the United States in which employ Americans. They did not even try to solve the problem of motivation based on KPI.in its US branches Japanese with the help of training successfully "copied" effective organizational culture and collective thinking of Japan.
As a result, the production data were "down" more effective local American businesses.it became clear that no KPI and other methods to stimulate labor are the basis of the productive work of the personnel and rational organizational culture and effective collective thinking.so from the 80s, transnational corporations in the world at the opening of new branches also began to use the training method as using KPI is not able to motivate staff on a harmonious and productive collective work.
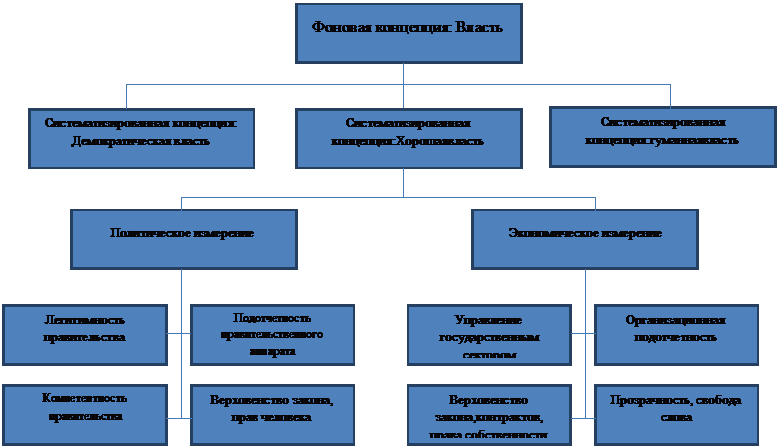
Добросовестное управление и международные рейтинги
В 2005 году международная правозащитная организация “Репортеры без границ” присвоили Сингапуру 140 позицию среди 167 стран в своем обзоре свободы прессы. Более низкие позиции заняли такие страны, как Судан (133-й) и Афганистан (125-й),что, в свою очередь, вызвало общественную дискуссию о ценности и обоснованности таких показателей.
Репортеры без границ является лишь одним из многих международных индексов, которые получили широкое распространение. Такие признанные организации как Организация Объединенных Наций, Всемирный Банк и многие другие академические и неправительственные организации разработали меры по определению количественных аспектов управления. Предоставляя правительствам эталонные тесты, для оценки их эффективности, они надеются продвигать практику «хорошей власти» для большего числа стран. Однако "хорошая власть" сама по себе является относительно молодой концепцией, которая до сих пор находится в процессе разработки.
Термин «эффективное управление» возник в конце 1980-х и начале 1990-х, прежде всего, во Всемирном Банке, который был обеспокоен тем, как власть влияет на экономические показатели. Эта первоначальная концепция эффективного управления включала такие факторы, как управление государственным сектором, организационную подотчетность, верховенство закона, прозрачность принятия решений, а также доступ к информации. Организация экономического сотрудничества и развития (ОЭСР) и Европейский союз затем интегрировали эту концепцию в свои требования поразвитиюсодействия.
Позже, Программа развития Организации Объединенных Наций (ПРООН) расширила определение для принятия политического измерения, которое включает в себя государственную легитимность, подотчетность правительства, компетентности правительства и защиты прав человека. В управлении в интересах устойчивого развития людских ресурсов (1997 год), ПРООН выделяет девять основных характеристик надлежащего управления: участие, верховенство закона, прозрачность, отзывчивость, консенсус ориентации, справедливости, эффективности и действенности, подотчетности и стратегического видения.
Европейская комиссия определила хорошее управление как "прозрачное и подотчетное управления ресурсами той или иной страны для ее справедливого и устойчивого экономического и социального развития».Аспекты эффективного управления включают в себя справедливость и верховенство права в управлении и распределении ресурсов; независимость и доступность судебной системы; и прозрачность. Коррупция определяется как основное препятствие для эффективного управления.
Кроме того, более широкое определение «хорошейвласти» обращает своё внимание на то, насколько хорошо правительство ориентируется на стратегические результаты, которые граждане ожидают от правительства. Эти стратегические результаты могут принимать форму определенных идеалов, таких как безопасной среды, прогрессивной экономики или здорового населения.
Рисунок 1: Схематическое представление управления