VIDEO TASKS:
1. Watch the video and answer the questions:
1. Describe the four basic shapes of bones.
2. Differentiate between the diaphysis and epiphyses of the long bones.
3. Differentiate between the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
4. Describe the role of the fontanels in protecting the infant brain.
5. List the five divisions of the vertebral column.
6. Name the three types of rib pairs seen in the thorax.
7. Name and describe the function of the six types of diarthrosis joints.

УРОК №4. МУСКУЛАТУРА ЧЕЛОВЕКА. MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Vocabulary:
| muscular tissue – мышечная ткань voluntary muscles – произвольно скоращающиеся мышцы involuntary muscles – непроизвольноскоращающиеся мышцы | Movements – движения contractile tissue – сокращающаяся ткань skeletal muscles – скелетные мышцы Cardiac muscle – сердечная мышца smooth muscles – гладкие мышцы Contraction – сокращение |
Muscular system is the system of Human Body that provides motor power for all movements of body parts. Muscular system is composed of special tissue called muscular tissue. Muscles have the ability to contract actively to provide the force for movements of body parts. Muscular system is an important system of human body because without it, life will completely stop. Muscles produce not only those movements that are under the control of our will and that we can see and feel, but also those movements that are responsible for activities like breathing, digestion of food, pumping of blood etc. Their function is to produce force and cause motion.
Functionally we divide all muscles into two groups: voluntary and involuntary muscles.
Muscle is a contractile tissue (сокращающаяся ткань) and is derived from the mesodermal layer (мезодермальный слой) of embryonic cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments (нити) that move past each other and change the size of the cell.
There are three types of muscle tissue. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth (гладкие) muscles.
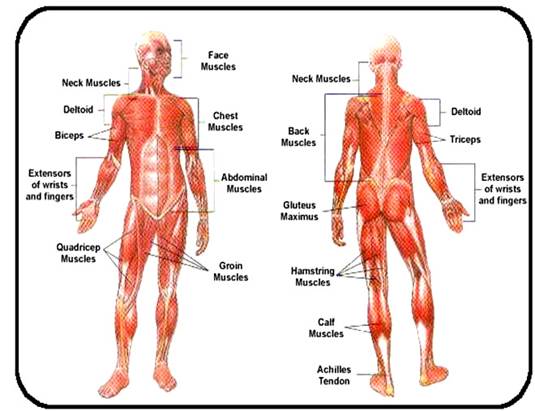
 Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" (произвольно сокращающаяся мышца) form most of the human body weight. They are under the control of human will and all body movements occurring by our will are produced by skeletal muscles. They are called skeletal muscles because they are almost always found attached to the skeleton and produce movements in different parts of the skeleton. An average adult male is made up of 42% of skeletal muscle and an average adult female is made up of 36%.
Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" (произвольно сокращающаяся мышца) form most of the human body weight. They are under the control of human will and all body movements occurring by our will are produced by skeletal muscles. They are called skeletal muscles because they are almost always found attached to the skeleton and produce movements in different parts of the skeleton. An average adult male is made up of 42% of skeletal muscle and an average adult female is made up of 36%.
Smooth muscle or "involuntary muscle" form the soft body organs like stomach, intestine, blood vessels uterus, urethra, bladder etc. They are not under the will of human beings and are responsible for unconscious body activities like digestion of food. They are called smooth muscles because when seen under the microscope, they do not have any striation in contrast to the other two types of muscles. 
 Cardiac muscle is also an "involuntary muscle" and is found only in the human heart. They are extremely strong and powerful muscles. They are not under the control of human will. The pumping of blood by human heart is because of the force provided by the contraction of cardiac muscles.
Cardiac muscle is also an "involuntary muscle" and is found only in the human heart. They are extremely strong and powerful muscles. They are not under the control of human will. The pumping of blood by human heart is because of the force provided by the contraction of cardiac muscles.
Answer the questions.
1. Give the definition of the word ‘muscle’.
2. What do muscle cells contain?
3. How are they classified?
4. What is a skeletal muscle?
5. What is a smooth muscle?
6. What is a cardiac muscle?
Muscular system has the following important functions in human body;
1. MOVEMENTS OF BODY PARTS: Skeletal muscles are responsible for all voluntary movements of human body parts. They provide the force by contracting actively. In other words, muscles are motors of body where chemical energy of food is converted into mechanical work.
2. STABILITY AND POSTURE: Skeletal muscles stabilize human skeleton and give a proper posture to human beings. Some joints of human body are weak and they require the support of muscular system to achieve stability. Skeletal muscles are very important for such joints.
3. HEAT PRODUCTION: A large share of body’s energy is used by muscular system. As a result of high metabolic rate, muscles produce great amount of heat in the body. Heat produced by muscles is very important in cold climates.
4. CIRCULATION: Cardiac muscles provide the main force for circulation of blood throughout human body. The regular pumping of heat keeps the blood in motion and nutrients are readily available to every tissue of human body.
5. HELP IN DIGESTION: Smooth muscles of organs like stomach and intestine help the digestive system in the process of digestion of food.
How a Muscle Works
A skeletal muscle works by CONTRACTING (getting shorter).
The muscle can shorten as much as 1/3 its resting length.
Each muscle cell is made up of many smaller MYOFIBRILS
The MYOFIBRILS are in contact with a nerve ending.
The nerve releases a chemical called a NEUROTRANSMITTER.
The Neurotransmitter stimulates the entire muscle cell to contract.
Muscles work in pairs. The biceps muscle will bend the arm at the elbow and the triceps muscle will straighten the arm. While one muscle in the pair contracts the other must relax.
Итоги:
| Components | Muscles: Muscles are special type of tissues of human body that posess the ability of contraction and relaxation. They can contract actively thus producing force for different body movements. | ||||||
| Types of Muscle |
| ||||||
| Functions | Movements of body parts, Stability and Posture, Heat production, Circulation, Help in Digestion |
VIDEO TASKS:
1. Give the four properties possessed by muscle tissue.
2. Differentiate between skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle.
3. Describe how muscles work together to create movement.
4. Discuss the ways in which skeletal muscle fiber cells differ from other cells in the body.
5. Describe the effects of strenuous exercise on the muscular system.
6. Tell how the terms "voluntary and "involuntary relate to muscular tissue.
УРОК №5. НЕРВНАЯ СИСТЕМА. NERVOUS SYSTEM
Vocabulary:
| Sensitivity – чувствительность Conductivity - электропроводность Responsiveness – восприимчивость Neuron - нейрон Central Nervous System (CNS) – центральная нервная система ЦНС Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – периферическая нервная система ПНС Brain – мозг spinal cord – спинной мозг the brain stem – мозговой ствол the cerebrum – головной мозг the cerebellum - мозжечок the diencephalon – промежуточный мозг glia - нейроглия grey matter – серой вещество white matter – белое вещество nerve fibers (axons) – нервное волокно | Medulla oblongata – продолговатый мозг the pons – варолиев мост hemisphere – полушарие Frontal lobe – лобная доля Temporal lobe – височная доля Parietal lobe – теменная доля Occipital lobe – затылочная доля the thalamus – таламус, зрительный бугор hypothalamus – гипоталамус, подбугорная область Somatic nervous system – соматическая нервная система Autonomic nervous system – вегетативная нервная система solid cords - твердый узел Spinal nerves – спинномозговые нервы Cranial Nerves – черепной нерв |
Nervous system is the chief controlling and coordinating system of the body. It controls and regulates all voluntary and involuntary activities of human body. There are three characteristic properties of nervous system of human body; Sensitivity, Conductivity and Responsiveness. The structural and functional unit (элемент) of nervous system is called neuron.
Parts of nervous system:
Nervous system of human body is divided into two parts: Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Central nervous system includes brain and spinal cord.
 The brain
The brain
The brain lies within the skull and is shaped like a mushroom. The brain consists of four principal parts:
the brain stem
the cerebrum
the cerebellum
the diencephalon
The brain weighs approximately 1.3 to 1.4 kg. It has nerve cells called the neurons and supporting cells called the glia.
 There are two types of matter in the brain: grey matter and white matter. Grey matter receives and stores impulses. Cell bodies of neurons and neuroglia (нейроглия) are in the grey matter. White matter in the brain carries impulses to and from grey matter. It consists of the nerve fibers (axons).
There are two types of matter in the brain: grey matter and white matter. Grey matter receives and stores impulses. Cell bodies of neurons and neuroglia (нейроглия) are in the grey matter. White matter in the brain carries impulses to and from grey matter. It consists of the nerve fibers (axons).
The brain stem is also known as the Medulla oblongata. It is located between the pons and the spinal cord and is only about one inch long.
The cerebrum forms the bulk (основная масса) of the brain and is supported on the brain stem. The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres. Each hemisphere controls the activities of the side of the body opposite that hemisphere. The hemispheres are further divided into four lobes: Frontal lobe, Temporal lobe, Parietal lobe, Occipital lobe.
The cerebellum is located behind and below the cerebrum.
The diencephalon includes the thalamus and hypothalamus. The thalamus is where sensory and other impulses go and coalesce (соединяться). The hypothalamus is a smaller part of the diencephalon.
The spinal cord is a long tube like structure which extends from the brain. The spinal cord is composed of a series of 31 segments. Both motor and sensory nerves are located in the spinal cord. The spinal cord is about 43 cm long in adult women and 45 cm long in adult men and weighs about 35-40 grams.
 Peripheral nervous system includes all the parts of nervous system except brain and spinal cord. It is further divided into two components: Somatic nervous system and Autonomic nervous system. The Somatic Nervous System is the part of the peripheral nervous system that handles (осуществлять) voluntary control of body movements. It contains all the neurons connected with skeletal muscles and skin.
Peripheral nervous system includes all the parts of nervous system except brain and spinal cord. It is further divided into two components: Somatic nervous system and Autonomic nervous system. The Somatic Nervous System is the part of the peripheral nervous system that handles (осуществлять) voluntary control of body movements. It contains all the neurons connected with skeletal muscles and skin.
The Autonomic Nervous System is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as an involuntary control system (below the level of consciousness), and controls visceral (висцеральный) functions.
Nerves:
Nerves are solid cords composed of bundles (узел) of nerve fibers (нервное волокно) (each nerve fiber is an axon with its coverings) bound together by connective tissue. Nerves are of two types: Spinal nerves and Cranial Nerves.
Spinal Nerves: Spinal nerves arise(брать начало) from the spinal cord. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves in human body.
Cranial Nerves Cranial nerves arise from the brain. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in human body
Functions of nervous system:
1. CONTROL OF ALL BODY FUNCTIONS: Nervous system is the master system of human body. It controls the activity of all other systems in such a way that all the systems collectively make a human being.
2. COORDINATION OF DIFFERENT BODY ORGANS: Nervous system not only produces coordination between different systems, but also between different organs of a system. So nervous system is not only important for formation of an organism by different organ systems, but also for formation of a system by different organs of human body.
Итого:
| Components |
| ||||||
| Divisions |
| ||||||
| Functions | Control of all body functions, Coordination of different body organs |
Exercises.
Answer the questions.
1. What parts does the nervous system consist of?
2. What is the central nervous system?
3. What does the peripheral nervous system consist of?
4. What parts does the brain consist of?
5. Where is the brain stem located?
6. How are the hemispheres divided?
7. Where is the cerebellum located?
8. What does the diencephalon include?
9. What do you know about the spinal cord?