Text#1 The Renaissance
This architectural style developed in early 15thcentury Italy during the rebirth of classical art and learning. It succeeded the Gothic as the style dominant in all of Europe after the mid 16thcentury into classicism.
Knowledge of the classical style in architecture was derived during the Renaissance from two sources: the ancient classical buildings, particularly in Italy but also in France and Spain and the treatise “De architectura” by the Roman architect Vitruvius. Initially it was characterized by the use of the classical orders, round arches, and symmetrical composition.
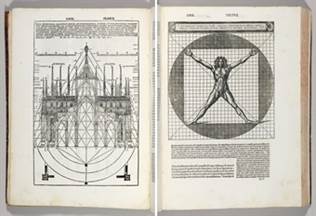 The Renaissance architects found a harmony between the proportions of the human body and those of their architecture. There was even a relationship between architectural proportions and the Renaissance pictorial device of perspective. The concern[1] of these architects for proportion caused that clear, measured[2] expression and definition of architectural space and mass that differentiates the Renaissance style from the Gothic and encourages[3] in the spectator an immediate and full comprehension of the building.
The Renaissance architects found a harmony between the proportions of the human body and those of their architecture. There was even a relationship between architectural proportions and the Renaissance pictorial device of perspective. The concern[1] of these architects for proportion caused that clear, measured[2] expression and definition of architectural space and mass that differentiates the Renaissance style from the Gothic and encourages[3] in the spectator an immediate and full comprehension of the building.
Churches, palaces, gardens, and well-organized open, urban spaces are the architectural works most often associated with this time. Great skill was expressed in ordering the interior of buildings, frequently using the same motifs as had been traditionally associated with the exterior.
 Filippo Brunelleschi[4] (1377-1446) is said to have created the Renaissance. In the early 15thcentury he formulated linear perspective, which was to become a basic element of Renaissance art. His basic vocabulary – fluted pilasters carrying entablatures[5], columns supporting arches, unribbed vaults which are portions of the surface of a sphere – appears in his brilliant work, Ospedale degli Innocenti[6] (1419-51) in Florence. It was the first building in the Renaissance manner.
Filippo Brunelleschi[4] (1377-1446) is said to have created the Renaissance. In the early 15thcentury he formulated linear perspective, which was to become a basic element of Renaissance art. His basic vocabulary – fluted pilasters carrying entablatures[5], columns supporting arches, unribbed vaults which are portions of the surface of a sphere – appears in his brilliant work, Ospedale degli Innocenti[6] (1419-51) in Florence. It was the first building in the Renaissance manner.

Answer the following questions.
1) When and where did the Renaissance begin?
2) What were the main sources of knowledge of the classical style in architecture?
3) What was the basic element of Renaissance art?
4) Who was the first to formulate and show the Renaissance system of perspective?
5) What was the first building in the Renaissance manner?
#2 Baroque
Baroque and late Baroque, or Rococo, are terms applied to European art of the period from the early 17thcentury to the mid 18thcentury.
The word “baroque” was derived from the Italian word “baroque”. This word also meant irregular or imperfect form, especially with reference to pearl.
The Baroque style is characterized by spatially complex compositions, interpenetration[7] of oval spaces, curved surfaces and remarkable use of decoration broken pediments, paired or coupled columns or pilasters. The Baroque art was essentially concerned with vivid[8] colours, hidden[9] light sources, luxurious materials and elaborate[10], contrasting surface textures. There was a tremendous richness of motifs-festoons of flowers and fruits, masks, scrolls, wreaths and weapons. During the Baroque period, architecture, painting and sculpture were integrated into decorative ensembles. Architects used sculpture to support the members of a building, painters decorated the walls and vaults of churches with false architectural perspectives, sculptors introduced colour in their works in the spirit of a painter.
 The Baroque rapidly developed into two separate forms: the strongly Roman Catholic counties (Italy, Spain, Portugal, Flanders, Bohemia, Southern Germany, Australia and Poland) tended toward freer and more active architectural forms and surfaces; in Protestant regions (England, the Netherlands and the remainder of Northern Europe) architecture was more restrained[11] and developed a quiet monumentality impressive in its refinement[12].
The Baroque rapidly developed into two separate forms: the strongly Roman Catholic counties (Italy, Spain, Portugal, Flanders, Bohemia, Southern Germany, Australia and Poland) tended toward freer and more active architectural forms and surfaces; in Protestant regions (England, the Netherlands and the remainder of Northern Europe) architecture was more restrained[11] and developed a quiet monumentality impressive in its refinement[12].
The greatest works of this style are Dome des Invalides by Hardouin-Mansart [13](1); the church of Santa Susanna (2); Versailles (3); Royal Palace in Madrid (4); Royal Palace at Caserta (5).


 1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
1) 2) 3) 4) 5)


1) 1)How is the word “Baroque” defined?
2) What are the main features of the Baroque?
3) What outstanding Baroque architects do you know?
Text #3 Rococo
The Rococo is assumed to have been the late phase of the Baroque, primarily French in origin. The style was first inspired by the shell-encrusted artificial fountains and grottoes at Versailles. This style refined the robust[14] architecture of the 17thcentury to suit elegant 18thcentury tastes. Vivid colours were replaced by pastel shades; diffuse[15] light flooded the building volume; violent surface relief was replaced by smooth flowing masses with emphasis only at isolated points. Churches and palaces still demonstrated an integration of the three arts, but the building structure was lightened to render interiors graceful and ethereal[16]. Rococo architects reduced column size to a minimum. In churches, the ceilings of side aisles were raised to the height of the nave ceiling unify the space from wall to wall.
The finest examples of the Rococo style are Church of the "Madonna del Carmine", Turin, Italy (1732); The Steinhausen Church of Pilgrimage, Germany (1728); Saint - Jacques, Luneville, France (1730)
Excellent examples of French Rococo are the Salon de Monsieur le Prince (completed 1722) in the Petit Château at Chantilly, decorated by Jean Aubert, and the salons (begun 1732) of the Hôtel de Soubise, Paris, by Germain Boffrand. The Rococo style was also manifested in the decorative arts. Its asymmetrical forms and rocaille ornament were quickly adapted to silver and porcelain, and French furniture of the period also displayed curving forms, naturalistic shell and floral ornament, and a more elaborate, playful use of gilt-bronze and porcelain ornamentation. In Italy the Rococo style was concentrated primarily in Venice, where it was epitomized by the large-scale decorative paintings of Giovanni Battista Tiepolo. The urban vistas of Francesco Guardi and Canaletto were also influenced by the Rococo. Meanwhile, in France the style had already begun to decline by the 1750s when it came under attack from critics for its triviality and ornamental excesses, and by the 1760s the new, more austere movement of Neoclassicism began to supplant the Rococo in France.
Questions
1) When did the Rococo appear?
2) What are typical characteristics of the Rococo?
3) What are differences between Rococo and Baroque?
#4 Industrial Design
 Industrial Design is an applied art whereby the aesthetics it improves usability of products. Design aspects specified by the industrial designer may include the overall shape of the object, the location of details with respect to one another, colour, texture, sounds, and aspects concerning the use of the product ergonomics. Additionally, the industrial designer may specify aspects concerning the production process, choice of materials and the presentation of a product to the consumer at the point of sale. Industrial designers make exclusive the visual design of objects. An industrial design consists of the creation of a shape, configuration or composition of pattern or colour, or combination of pattern and colour in three-dimensional form containing aesthetic value.
Industrial Design is an applied art whereby the aesthetics it improves usability of products. Design aspects specified by the industrial designer may include the overall shape of the object, the location of details with respect to one another, colour, texture, sounds, and aspects concerning the use of the product ergonomics. Additionally, the industrial designer may specify aspects concerning the production process, choice of materials and the presentation of a product to the consumer at the point of sale. Industrial designers make exclusive the visual design of objects. An industrial design consists of the creation of a shape, configuration or composition of pattern or colour, or combination of pattern and colour in three-dimensional form containing aesthetic value.
The use of industrial designers in a product development process improves usability, lowers production costs and leads to the appearance of more appealing products. It is important that in order to be an Industrial Design the product has to be produced in an industrial way, for example, an artisan[17] cannot be considered an industrial designer, although he may challenge the same aspects of a product.
Some industrial designs are viewed as classic pieces that can be regarded as much as work of art as works of engineering.
 Industrial design has a focus on concepts, products and processes. In addition to aesthetics, usability and ergonomics, it can also include the engineering of objects, usefulness as well as usability, market placement and other concerns.
Industrial design has a focus on concepts, products and processes. In addition to aesthetics, usability and ergonomics, it can also include the engineering of objects, usefulness as well as usability, market placement and other concerns.
Answer the questions to the text:
1) What is industrial design? What does it deal with?
2) What does industrial design help to improve?
3) What aspects does an industrial designer usually pay attention to?
4) What does industrial design have focus on?
#5 High-tech style
Features
High-tech style embraces an industrial look, in which the decor and the building itself are obviously very influenced by technology. High-tech buildings are often created from such materials as heavy steel girders[18], a metal deck plate[19], metal shelves often seen in hospitals and factories, and a concrete structure. The outside of the building, instead of being opaque[20], is often made entirely of windows or mirrored glass, not stressing the decorative outside of the building but revealing the skeleton of the building itself.
Examples
High-tech style can be seen in almost any city in the world.

 One of the most well-known examples of high-tech style is the Swiss Re building [21] in London – more commonly known as The Gherkin[22], because of its distinctive, peaked shape. Designed by British architect Norman Foster, the building is the sixth tallest in London, and stands out from the background of centuries-old buildings from miles around. The Gherkin was opened in 2004, and has been featured in a number of television shows and movies, quickly becoming one of London's most recognized modern symbols. Also in London is the Lloyd's Building, which is unique as all of its staircases, elevators, ventilation shafts and piping are on the outside of the building.
One of the most well-known examples of high-tech style is the Swiss Re building [21] in London – more commonly known as The Gherkin[22], because of its distinctive, peaked shape. Designed by British architect Norman Foster, the building is the sixth tallest in London, and stands out from the background of centuries-old buildings from miles around. The Gherkin was opened in 2004, and has been featured in a number of television shows and movies, quickly becoming one of London's most recognized modern symbols. Also in London is the Lloyd's Building, which is unique as all of its staircases, elevators, ventilation shafts and piping are on the outside of the building.
History
High-tech style made its first appearances after World War II. Much of Europe – from England all the way across the continent – had been ravaged[23] by war, leaving countless buildings destroyed. When the time came to rebuild, designers and architects replaced many of the old edifices[24] with ones done in a forward-thinking, new style that was intended to show something new rising from the ashes of destruction.
Significance
High-tech style came about when architects and designers were looking for a way to liven up modern architecture. In many places, any sort of modern architecture had been replaced with economy buildings. Technological advances were on everyone's mind, and this high-tech style leaned away from traditional architecture and more toward science fiction and the world of tomorrow.
Answer the questions.
1) When did the high-tech style appear?
2) What are the typical features of this style?
3) What are the most famous architectural models constructed in this style?
[1] сoncern – внимательное отношение
[2] measured - размеренный
[3] encourages – зд. вдохновляет, вызывает
[4] Филиппо Брунеллески (1377—1446) — итальянский архитектор, скульптор эпохи Возрождения.
[5] entablature - антаблемент
[6] Воспитательный дом (итал. Ospedale degli Innocenti) — приют для бездомных детей во Флоренции
[7] interpenetration - взаимопроникновение
[8] vivid - яркий
[9] hidden - скрытый
[10] elaborate – тщательно разработанный
[11] restrained - сдержанный
[12] refinement - утонченность
[13] Собор Дома Инвалидов, архитектор Жюль Ардуэн-Мансар (1646—1708)
[14] robust - грубоватый
[15] diffuse – рассеянный
[16] ethereal - лёгкий, воздушный; деликатный, утончённый, изысканный
[17] an artisan – кустарь, мастеровой, ремесленник
[18] girders - балки
[19] a metal deck plate – металлическая палубная втулка
[20] opaque – матовый, непрозрачный
[21] The Swiss Re building (the building of Swiss Reinsurance Company) = 30 St Mary Axe
[22] a gherkin - корнишон
[23] to ravage – опустошать, разорять
[24] an edifice - большой дом