TEXT A. WHAT IS A СONFERENCE?. 40
TEXT B. PREPARATION FOR A CONFERENCE.. 41
GRAMMAR REVISION.. 57
Passive Voice. 57
Passive and Active Compared. 60
Participle II 64
Rronouns. 66
Word order 73
ПРАКТИЧЕСКИЙ РАЗДЕЛ
М-2Социокультурная сфера общения. Я и межкультурная коммуникация
UNITI
TEXT A
HIGHER EDUCATION IN GREAT BRITAIN
VOCABULARY INDEX
| NOUNS | |
| 1. agribusiness | агропромышленный комплекс, агробизнес |
| 2. agriculture | сельское хозяйство |
| 3. agricultural | сельскохозяйственный |
| 4. BachelorofArts, Science | бакалавр гуманитарных наук, технических наук |
| 5. completion | завершение, окончание |
| 6. course sandwichcourse | курс (период учебы); курс обучения, чередующий теорию с практикой |
| 7.dean | декан |
| 8. direction under the direction | руководство, управление; под руководством: |
| 9. division | деление, разделение |
| 10. employment | занятие, работа |
| 11. examination (exam) finalexam | экзамен выпускной экзамен |
| 12. extensionservice | служба распространения знаний и опыта |
| 13. farm | хозяйство, ферма |
| 14. farmer | фермер |
| 15. farming | земледелие, сельское хозяйство |
| 16. graduation | окончание, получение диплома |
| 17. higher education | высшее образование |
| 18. higher educational institution syn. establishment | высшееучебноезаведение |
| 19.Master of Arts, Science | магистр гуманитарных наук, технических наук |
| 20.opportunity | возможность |
| 21. production | производство |
| 22. purpose | назначение, намерение, цель |
| 23.qualification | квалификация |
| postgraduate | аспирант |
| 24.range | ряд |
| 25. science animal science crop science | наука; зоотехния; растениеводство |
| 26. scholarship | стипендия |
| 27. term | семестр |
| 28. thesis syn. originalpaper | диссертация |
| 29. tutorial | консультация |
| 30. undergraduate | студент, еще не получивший диплом |
| VERBS | |
| 1. accompany | сопровождать, сопутствовать |
| 2. alternate | сменять друг друга, чередоваться |
| 3. carry out | проводить |
| 4. contain | содержать, вмещать |
| 5. correspond | соответствовать |
| 6. design | проектировать, конструировать |
| 7. employ | нанимать, давать работу |
| 8. encompass | выполнять, осуществлять |
| 9. offer | предлагать |
| 10. pass exams | сдавать экзамены; |
| 11. provide | обеспечивать, снабжать |
| 12. raise | поднимать |
| 13. regard | рассматривать, считать |
| 14. select | отбирать, выбирать |
| ADJECTIVES | |
| 1. academic | учебный |
| 2. advanced | продвинутый |
| 3. full-time | дневной |
| 4. part-time | занятый неполное время (вечерний) |
| 5. research | научно-исследовательский |
| 6. specialized | специализированный |
| 7. superior | превосходящий |
| 8. worldwide | повсемумиру |
READING
|
|

Part I
With outstanding teaching and facilities, UK universities and colleges offer a world-class higher education and qualifications that are respected by employers and academics worldwide.
In England, Wales and Northern Ireland, higher education institutions are independent, self-governing bodies active in teaching, research and scholarship. They are established by Royal Charter or legislation and most are part-funded by government.
 English universities greatly differ from each other. They differ in date of foundation, size, history, tradition, general organization, methods of instruction, and way of student life.
English universities greatly differ from each other. They differ in date of foundation, size, history, tradition, general organization, methods of instruction, and way of student life.
There are forty-seven universities in Britain and thirty former polytechnics (now also universities), plus 350 colleges and institutes of higher education. The oldest and best-known universities are located in Oxford, Cambridge, London, Leeds, Manchester, Liverpool, Edinburgh, Southampton, Cardiff, Bristol, Birmingham.
UK higher education is split into two levels:
· Undergraduate programmes include bachelor’sdegrees, foundation degrees, higher national diplomas and more.
· Postgraduate programmes include master’sdegrees, MBAs (Master of Business Administration), PhDs (Doctor of Philosophy), doctoratesand more. Usually you need an undergraduate qualification to enter a postgraduate programme.
After three years of study a university graduate will leave with the Degree of Bachelor of Arts, Science, Engineering, Medicine, etc. Later he may continue to take Master's Degree and then a Doctor's Degree. It goes without saying it that research is an important feature of university work.
Most full-time undergraduate courses take three years to complete (typically four years in Scotland). Full-time postgraduate courses can be from one year upwards.
 Part-time courses are normally taken over a longer period, so that you can work alongside your studies or learn at a more relaxed pace. There is no set length of time for part-time courses – it varies from one course to another.
Part-time courses are normally taken over a longer period, so that you can work alongside your studies or learn at a more relaxed pace. There is no set length of time for part-time courses – it varies from one course to another.
|
|
Good A-level results in at least 2 subjects are necessary to get a place at a university. However, good exam passes alone are not enough. Universities choose their students after interviews. For all British citizens a place at a university brings with it a grant from their local education authority.
The academic year in Britain's universities and Colleges of education is divided into 3 terms, which usually run from the beginning of October to the middle of December, the middle of January to the end of March, from the middle of April to the end of June or the beginning of July.
 The university teachers hold university appointments as lecturers or professors. Part of the teaching is by means of lectures and any student may attend any university lecture. At the beginning of each term a list is published showing all the lectures being given during the term within each faculty, and every student can choose which lectures he will attend, though his own college tutor will advise him which lectures seem likely to be more useful. Attendance at lectures is not compulsory, and no records of attendance are kept.
The university teachers hold university appointments as lecturers or professors. Part of the teaching is by means of lectures and any student may attend any university lecture. At the beginning of each term a list is published showing all the lectures being given during the term within each faculty, and every student can choose which lectures he will attend, though his own college tutor will advise him which lectures seem likely to be more useful. Attendance at lectures is not compulsory, and no records of attendance are kept.
Apart from lectures, teaching is by means of the “tutorial” system, which is a system of individual tuition organized by the colleges. Each teacher in a college is tutor in his own subject to the undergraduates who are studying it. Each student goes to his tutor’s room once every week to read out an essay which he has written, and for an hour he and the tutor discuss the essay.
Part II
Agricultural education encompasses the study of applied sciences (e.g., biology, chemistry, physics), and business management principles. One of the major purposes of agricultural education is to apply the knowledge and skills learned in several different disciplines to agricultural education.
 Agricultural engineers use their knowledge to solve the problems of farmers and the agricultural industry. They work to improve the quality and increase the production of farm products. Most agricultural engineers work for manufacturing companies that design and supply equipment. In these companies engineers work in sales, research and development, marketing, advertising, and management. Some engineers teach in colleges and universities. Others work as technical writers and editors for agricultural publications. Engineers also do extension service work or work for banks or insurance companies. A few are self-employed as consultants to farmers, manufacturers, and government agencies.
Agricultural engineers use their knowledge to solve the problems of farmers and the agricultural industry. They work to improve the quality and increase the production of farm products. Most agricultural engineers work for manufacturing companies that design and supply equipment. In these companies engineers work in sales, research and development, marketing, advertising, and management. Some engineers teach in colleges and universities. Others work as technical writers and editors for agricultural publications. Engineers also do extension service work or work for banks or insurance companies. A few are self-employed as consultants to farmers, manufacturers, and government agencies.
 Agricultural engineers generally specialize in one of five major areas: farm structures, mechanical power, electrification, soil and water conservation, and food engineering. Engineers who work in farm structures design farmhouses, barns and other animal shelters, and crop storage facilities such as silos and granaries. In addition, they plan sanitation, ventilation, and heating systems for these buildings. Agricultural engineers also design power machines used on farms for land tilling, insect control, fertilization, and harvesting.
Agricultural engineers generally specialize in one of five major areas: farm structures, mechanical power, electrification, soil and water conservation, and food engineering. Engineers who work in farm structures design farmhouses, barns and other animal shelters, and crop storage facilities such as silos and granaries. In addition, they plan sanitation, ventilation, and heating systems for these buildings. Agricultural engineers also design power machines used on farms for land tilling, insect control, fertilization, and harvesting.
|
|
 Agricultural engineers involved in electrification may design an electric power system for a rural region. Others develop or improve ways to use electric power for such purposes as curing and drying crops or dehydrating food. Engineers who work in soil and water conservation develop irrigation, drainage, and flood control systems. The newest specialty of agricultural engineers is that of food processing. In this work, engineers design efficient food plants and new machinery to preserve, package, and distribute foods.
Agricultural engineers involved in electrification may design an electric power system for a rural region. Others develop or improve ways to use electric power for such purposes as curing and drying crops or dehydrating food. Engineers who work in soil and water conservation develop irrigation, drainage, and flood control systems. The newest specialty of agricultural engineers is that of food processing. In this work, engineers design efficient food plants and new machinery to preserve, package, and distribute foods.
LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT

(A) Exercise 1.Give the English equivalents for the following words and word combinations.
· высшее образование мирового уровня;
· высшее учебное заведение;
· студент, не получивший диплом;
· сельскохозяйственное образование;
· аспирант;
· бакалавр технических наук;
· магистр гуманитарных наук;
· обучение на дневном отделении;
· обучение на вечернем отделении;
· ученая степень;
· трехгодичные курсы;
· квалификация;
· выпускные экзамены;
· доктор философских наук.


(B) Exercise 2. Match the word with the definition.
| 1) university | a) a system of individual tuition organized by the colleges |
| 2) highereducation | b) include bachelor’s degrees, foundation degrees, higher national diplomas |
| 3) scholarship | c) an institution of higher education and research which grants academic degrees in various subjects |
| 4)undergraduate programmes | d) teaches students about agriculture, food and natural resources |
| 5) postgraduate programmes | e) an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after secondary education |
| 6) term | f)a period of study at a higher educational establishment |
| 7) degree | g) include master’s degrees, MBAs, PhDs, doctorates |
| 8) tutorialsystem | h) an academic qualification awarded at universities upon the completion of a higher educational course |
| 9) agricultural education | i) a person who gives lectures |
| 10) lecturer | j)an award of financial aid for a student to further their education |
(B) Exercise 3. Match the words. Compose sentences with the obtained phrases.
| attend | programm |
| higher | exams |
| award | lectures |
| undergraduate | Arts |
| pass | education |
| Doctor of | Philosophy |
| Bachelor of | degrees |
 (B) Exercise 4.Read the sentence pair. Choose where the words best fit in the blanks.
(B) Exercise 4.Read the sentence pair. Choose where the words best fit in the blanks.
1) degree/ scholarship
A) His purpose was to get Bachelor’s _______.
B) To be financially independent it is important to get a _______.
2 ) tutor/lecturer
A) Each student goes to his _______ once every week to read out an essay which he has written.
B) A _______ doesn’t keep any records of attendance.
3) Doctor of Philosophy / Bachelor’s degree
A) A _______ is the highest academic level a student can achieve.
B)_______ is an academic study designed to help you gain a thorough understanding of a subject. Full-time, this normally takes three years to complete.
4) full-time/part-time
A) It takes three years to complete most _______undergraduate courses.
B)_______ courses are normally taken over a longer period.
C) Exercise 5. Find a word in the text that means the same as:
1) a complete period of studies;
2) courses in which you can work alongside your studies or learn at a more relaxed pace;
3) academic qualification awarded at universities upon the completion of a higher educational course;
4) an individual class with a tutor;
5) a talk with the university authorities the purpose of which is to be admitted to a university;
6) a process of studying a scientific problem.

TEXT STUDY

(A) Exercise 1. Complete each sentence with an appropriate word. Consult text A if necessary.
1. UK … and colleges offer a world-class higher education.
a) schools;
b) institutions;
c) universities.
2. Higher education institutions are independent, self-governing bodies active in teaching and …
a)research;
b) knowledge;
c)education.
3. Good A-level results in at least 2 … are necessary to get a place at a university.
a) seminars;
b) subjects;
c) lectures.
4. The academic year in Britain's universities is divided into 3 …
a) disciplines;
b)terms;
c) periods.
5. After three years of study a university graduate will leave with the Degree of …
a) Doctors of Philosophy;
b) Masters of Arts or Science;
c) Bachelor of Arts or Science.
6. Any student may attend any university …
a) lecture;
b) exam;
c)tutor’s room.
(A) Exercise 2. Complete each sentence with the appropriate ending.

| A | B |
| 1. The universities in Great Britain … | a) the most famous British universities. |
| 2. Universityteachingcombines… | b) they get their first degree and become Bachelors of Arts or Sciences. |
| 3. Studies in courses may be … | c) are part-funded by government. |
| 4. There is no set length of time for | d) they have to take a postgraduate course. |
| 5. If students pass their final exam at the end of a three-year course … | e)lecturesandtutorials. |
| 6. If they want to become Masters of Arts or Science… | f) full-time and part-time. |
| 7. Oxford and Cambridge are … | g) part-time courses. |
(B) Exercise 3. Read the questions below and see if you can answer them without consulting the text. If you need, find the information in the text.

1. What kind of education do the universities in Great Britain provide?
2. How do the English universities differ from each other?
3. What are the two levels of UK higher education?
4. What is the difference between full time and part time courses?
5. How does the tutorial system work?
6. What degree is awarded after passing final exams at the end of three-year courses?
7. What do students have to do to become a Master of Arts or Science?
8. Who is a Doctor of Philosophy?
9. What are the most famous universities in Great Britain?
(B) Exercise 4. Define whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false ones.
1. Qualifications offered at UK universities and colleges are not recognized by employers and academics worldwide.
2. The oldest and most famous universities are located in Oxford, Cambridge, London, Leeds, Manchester, Liverpool, Edinburgh, Southampton, Cardiff, Bristol, Birmingham.
3. Postgraduate programmes include bachelor’sdegree.
4. Most full-time undergraduate courses take three years to complete.
5. If students pass their final exam at the end of a three-year course, they become Masters of Arts or Science.
6. Attendance at lectures is compulsory.
7. Full-time postgraduate courses can be from two years on.
B) Exercise 5. Divide the text into logical parts and entitle them.
(B) Exercise 6. Give the main idea of the text (6 – 8 sentences).
(B) Exercise 7. Match these phrases with the text. Where exactly does each phrase go in the text?
| a) lectures | e)students |
| b) the tutorial system | f) lead a discussion |
| c) the tutor | g) a federation of individualcolleges |
| d) prestigious | h) the subject |

The University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge are two of the most 1)… universities in the world. Both Oxford and Cambridge are 2)…, each with its own faculty, administrators, grounds, residence halls and traditions. Students apply directly to a college, rather than to the universities. The hallmark of Oxbridge academics is 3)…. The tutorial is typically a one-hour meeting between one or two students and 4)….. Typically tutorials meet once a week orevery other week, and center on an essay on a topic previously assigned. The tutor will 5)… about the essay topic in an effort to provide new insights. At the end of the session, you will be assigned a new topic and may be offered recommended reading. Tutorials are individually arranged, taking into account 6)… to be studied and the tutor's area of expertise. This system is ideal for hard-working, independent 7)… who are passionate about academics. Each university also organizes weekly 8)… on various academic subjects that all students at the University are welcome to attend, and they are often recommended by Tutors as good supplements to tutorials and research.

(В) Exercise 8. Speak about:
a) types of higher education institutions in Great Britain;
b) a variety of courses the universities provide;
c) academic classes;
d) full-time education;
e) academic qualifications.
(С) Exercise 9. Explain the difference between:
a) lectures and tutorials;
b) full-time and part-time education;
c) Bachelors of Science and Masters of Science;
d) an original paper and term paper.
(С) Exercise 10. Discuss the main points of the text with your group mates. Use the following prompts.
1. What is … about?
2. In what way is the term “part-time courses” defined?
3. How can you describe …?
4. In what way is … organized?
5. What is a tutorial?
(C) Exercise 11. Choose someone to act as a member of Students’ Youth Organization. Answer the visitor’s questions.
| What is (are)…? | higher education institution |
| Could you explain to me…? | postgraduate programmes |
| Can you tell me about…? | Bachelor’s degree |
| What do you mean by…? | the most famous universities |
| Why…? | the difference between full-time and part-time education |
| Where do (does)…? | university teaching |
(C) Exercise 12.Make an annotation and summary of part II of the text.

SPEAKING

(А) Exercise 1. Complete the table and the logical diagram with the necessary information from the text.
| First degree | On completion of a three-year course | |
| Higher degrees | ||
| Doctor of Philosophy |
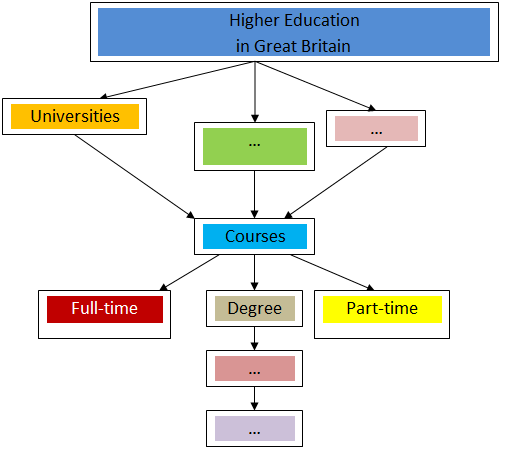
(A) Exercise 2. Speak about the system of higher education in Great Britain. Use the logical diagram.
(B) Exercise 3. Speak about the differences and similarities in the system of higher education in Great Britain and in Belarus.
(B) Exercise 4. Compare the degrees that are awarded at universities in Belarus and Great Britain.
(C) Exercise 5. You are a foreign guest in Great Britain. Your English friend wants to take you to one of British universities. Say what university you would like to see and why. Say what you know about this university.

TEXT B
OUR UNIVERSITY
VOCABULARY INDEX
NOUNS

| |
| 1. academician | академик |
| 2. apparatus training apparatus | гимнастический снаряд тренажер |
| 3.associate professor | доцент |
| 4. corresponding member of the Belarusian Academy of Sciences | член-корреспондент Национальной академии наук Беларуси |
| 5. credit | зачет |
| 6. faculty syn. department | факультет |
| 7. agro-mechanical | агромеханический |
| 8. agro-power | агроэнергетический |
| 9. business and management | предпринимательство и управление |
| 10. engineering and technology | инженернотехнологический |
| 11. farm machinery service | технический сервис |
| 12. campus | университетский городок |
| 13. canteen | столовая |
| 14. curriculum | курс обучения, учебный план (института, университета) |
| 15. disposal to be at the disposal of smb. | возможность распорядиться чем-либо/ быть в чьем-то распоряжении |
| 16. entrance entrance examinations | вход, прием, поступление вступительные экзамены |
| 17. engineer | инженер |
| 18. mechanic engineer | инженер-механик |
| 19. engineers for electrification and automation of farm production | инженер по электрификации и автоматизации с/х производства |
| 20. farm machinery maintenance engineer | инженер по ремонту с/х машин |
| 21. facilities | оборудование, благоприятные условия |
| 22. fee | плата за учение |
| 23. graduate | выпускник |
| 24. guidance under the guidance of | руководство под руководством |
| 25. hostel syn. dormitory | общежитие |
| 26. record book | зачетная книжка |
| 27. scholarship | стипендия |
| 28. science | наука |
| 29. speciality | специальность |
| 30. staff teaching staff | штат, сотрудники преподавательский состав |
| 31. training | обучение |
| 32. turf artificial turf | дерн искусственное покрытие |
| 33. workshop | мастерская |
VERBS

| |
| 1. admit | принимать |
| 2. attend | посещать |
| 3. be in one’s first (second, …) year / to be a first (second, …) year-student | быть на первом (втором, …) курсе / быть студентом первого (второго…) курса |
| 4. carryout | выполнять |
| 5. conduct | проводить, вести |
| 6. get ready for syn. to prepare for | готовиться к чему-либо |
| 7. graduatefrom | оканчивать, заканчивать учебное заведение |
| 8. enrol(l) | зачислять |
| 9. enter a university | поступать в университет |
| 10. fail (a test or exanination) in (e.g. physics) syn. flunk | провалить (тест, экзамен) по (напр. физике) |
| 11. found | основывать |
| 12. master | изучать, овладевать |
| 13. miss (classes) | пропускать (занятия) |
| 14. passexams | выдержать (сдать) экзамен |
| 15. swot | зубрить |
| 16. takeexams | сдавать экзамен |
| 17. take a course (subject) | изучать курс (предмет) |
| 18. takenotesofsmth | делать заметки, записывать, конспектировать |
ADJECTIVES

| |
| 1. advanced | продвинутый, успевающий (о студенте) |
| 2. artificial | искусственный |
| 3. compulsory | обязательный |
| 4. educative | образовательный |
| 5. extra-curricular | внеаудиторный |
| 6. extra-mural syn. correspondence | заочный |
| 7. optional | необязательный, факультативный |
| 8. scientific | научный |
PRE-READING TASK
