
Match the names with descriptions. There is one extra name.
| 1. a biological system containing a network of specialized cells | 2. consists of sensory neurons, clusters of neurons called ganglia, and nerves | 3. forms the bulk of the brain and is supported on the brain stem. | 4. is divided into two major parts: the brain and the spinal cord. |
| 5. lies within the skull and is shaped like a mushroom. | 6. is located behind and below the cerebrum. | 7. is a long tube like structure which extends from the brain. |
a. the brain
b. the cerebrum
c. the spinal cord
d. the central nervous system
e. the peripheral nervous system
f. the cerebellum
g. the diencephalon
h. the nervous system
| Video tasks: 1. List the organs of the nervous system. 2. Differentiate between the central and peripheral nervous systems. 3. Name the two types of cells in the nervous system. 4. Name the structures that make up a neuron. 5. Differentiate between the three main types of neurons. 6. Describe the role of the cerebral spinal fluid. 7. Discuss the function of the autonomic nervous system. |
УРОК №7. СЕРДЕЧНОСОСУДИСТАЯ СИСТЕМА. CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Vocabulary:
| to pump - качать approximately - приблизительно to remove the waste products – удалять использованные продукты cardiac cycle – сердечный цикл cavity - полость chambers - камеры atria - предсердие | ventricle - желудочек superior vena cava – верхняя полая вена inferior vena cava – нижняя полая вена coronary sinus – коронарный синус right atrioventicular valve – правый предсердно-желудочковый клапан | reoxygenated – перенасыщать кислородом pulmonary veins – лёгочные вены to nourish - питать blood stream - кровоток cardiac output – минутный объем сердца |
Read and translate the scientific text using the vocabulary.
The cardiovascular system is the system of blood circulation. By the cardiovascular system we mean the heart, the arteries, the veins and the capillaries of the human body.
The centre of the circulatory system is the heart. The heart is one of the most important organs in the human body. It pumps blood throughout the body, beating approximately 72 times per minute of our lives. The heart pumps the blood, which carries all the vital materials which help our bodies function and removes the waste products that we do not need.
The heart is a muscle. Like any other muscle in the human body, it contracts and expands. Each time the heart contracts it does so with all its force. In skeletal muscles, the principle of "gradation" is present. The pumping of the heart is called the Cardiac Cycle, which occurs about 72 times per minute. This means that each cycle lasts about eight-tenths of a second. During this cycle the entire heart actually rests for about four-tenths of a second.
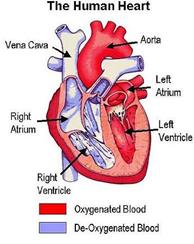
Make-up of the Heart
The walls of the heart are made up of three layers, while the cavity is divided into four parts. There are two upper chambers, called the right and left atria, and two lower chambers, called the right and left ventricles. The Right Atrium, as it is called, receives blood from the upper and lower body through the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and from the heart muscle itself through the coronary sinus.
The right atrium is the larger of the two atria, having very thin walls. The right atrium opens into the right ventricle through the right atrioventicular valve. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs to be reoxygenated. The left atrium receives blood from the lungs via the four pulmonary veins. It is smaller than the right atrium, but has thicker walls. The left ventricle pumps the blood throughout the body. It is the Aorta, the largest artery in the body, which originates from the left ventricle.
The Heart works as a pump moving blood around in our bodies to nourish every cell. Blood that has been reoxygenated by the lungs is drawn into the left side of the heart and then pumped into the blood stream. It is the atria that draw the blood from the lungs and body, and the ventricles that pump it to the lungs and body. The output of each ventricle per beat is about 70 ml, or about 2 tablespoons. In a trained athlete this amount is about double. With the average heart rate of 72 beats per minute the heart will pump about 5 litres per ventricle, or about 10 litres total per minute. This is called the cardiac output.
|