There are numbers having exactly two factors, 1 and the number itself. They are called prime numbers or primes. For example, the numbers 5, 37, 111, 1093 can be divided only by 1 and themselves.
The number 1 has only one factor that’s why it is not a prime.
Every natural number bigger than 1 is either a prime or can be written as a product of primes. For example, 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2; 17 is a prime; 44 = 11 × 2 × 2; 53 is a prime.
All real numbers are rational or irrational.
The number is rational if it can be written in the form 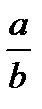 where b ≠ 0 and ‘ a ’ and ‘ b ’ are integers. Examples of rational numbers: 3; -2;
where b ≠ 0 and ‘ a ’ and ‘ b ’ are integers. Examples of rational numbers: 3; -2;  ; 0,1; 4,(3); 6
; 0,1; 4,(3); 6 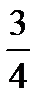 .
.
Irrational numbers cannot be written as a fraction. These are square roots of non-square numbers, cube roots of non-cube numbers, the number π and surds. Example of irrational numbers: 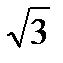 ,
,  , π.
, π.
A surd is a root of rational number which cannot be expressed as rational number, e.g. 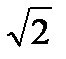 ,
, 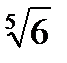 .
.
Vocabulary
prime [praim] простое число
rational number [′rxSən(ə)l] рациональное число
irrational number [i′rxSən(ə)l] иррациональное число
exactly [ig'zxktli] точно
number itself само число
natural number [′nxCr(ə)l nAmbə(r)] натуральное число
either … or… [′aiðə(r) Lr] или…или…
surd [sə:d] иррациональное число, выраженное в радикалах
root [ru:t] корень
square root [skweə ru:t] корень квадратный
cube root [kju:b ru:t] корень кубический
π [pai] число π (3,14)
to express [iks′pres] выражать
that’s why поэтому
Task 1. Answer the questions.
1. What is a prime?
2. What is a rational number? Irrational number?
3. What is a surd?
Task 2. Define which of the numbers are a/ primes, b/ rational numbers, c/ irrational numbers:
5,5; 13;  ;
;  ; 0,666…; 0; 59;
; 0,666…; 0; 59; 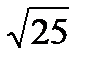 ; e; 7,125;
; e; 7,125;  ;
; 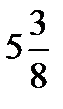 ; -9,02; 19; 0,3131...;
; -9,02; 19; 0,3131...; 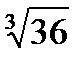 . Why do you think so?
. Why do you think so?
Task 3. Give your own examples of primes, rational and irrational numbers. Prove that your choice is true. Use information from the text.
Task 4. Render the text.
Text 14
EQUATIONS
Equation is an algebraic expression to state equality of two numbers or quantities. For example, ‘ a + 4 = 6’ is an equation stating that ‘ a + 4’ equals ‘6’. The letter ‘ a ’ stands for an unknown (number or quantity).
To solve an equation means to find the numerical value of the letter which fits the equation. This value is called the root or the solution of the equation.
In maths two kinds of equations are differed: conditional equations (= equations) and identical equations (= identities).
In an identity both terms (= sides) are equal for all values of the unknown number (or numbers), e.g. (x + y)2 = x 2 +2 xy + y 2.
Sometimes the symbol ≡ (equivalent) is used to distinguish an identity from a conditional equation
If two equations have the same root, they are called equivalent equations, e.g. ‘ a + 6 = 9’ and ‘2 a + 3 = 9’ are equivalent since they both have the single root ‘ a = 3’.
An equation of the form ‘ ax + b = 0’ where a ≠ 0 is an equation of the first degree in the unknown x, or simple linear equation
There are also quadratic equations (like y 2 = 4), cubic equations, and integral equations that involve an integral of a function.
Vocabulary
equation [i′kveiS(ə)n] уравнение
to state [steit] утверждать
equality [i′kwOliti] тождество, равенство
quantity [′kwOntiti] количество
to stand for [stxnd fO(r)] обозначать
unknown [An′nəun] неизвестное
to solve [sOlv] решать
to mean [mi:n] значить
numerical value [nju′merik(ə)l ′vxlju:] числовое значение
to fit [fit] подходить, удовлетворять
root [ru:t] корень
solution [sə′lu:S(ə)n] решение
kind [kaind] вид
side [said] сторона
to differ [′difə(r)] различать, отличать
conditional equation [kən′diSən(ə)l i′kweiS(ə)n] условное уравнение
identity [ai′dentiti] тождество
both [bəuT] оба
true [tru:] верный, правильный, истинный
equivalent [i′kwivələnt] эквивалентный
since [sins] так как
single [siNg(ə)l] один, единственный
to distinguish [dis′tiNgwiS] отличать, различать
the first degree [Də fə:st di′gri:] первая степень
linear equation [′li:niə(r)] линейное уравнение
in the unknown [in Də An nəun] с одним неизвестным
quadratic [kwOd'rxtic] квадратный
cubic ['kjubic] кубический
to involve [in'vOlv] включать в себя
integral [′intigr(ə)l] интеграл, интегральный
function [′fAnkS(ə)n] функция
Task 1. Complete the sentences.
1. Equation is an algebraic expression to state …
2. In the expression ‘ x + 3 = 5’ the letter ‘ x ’ stands for …
3. To solve an equation means …
4. Two types of equations are …
5. In an identity both terms are …
6. In a linear conditional equation only …
7. Equivalent equations have …
8. There are not only linear equation but …
Task 2. Give your own examples of equations of different kinds.
Text 15