| А | |
| allowable | 2.1.2.6 |
| allowable operating range | 2.2.1.3, 2.1.13.3 |
| allowable temperature range of the pump | 2.1.10.2 |
| allowable working | 2.1.2.7.2 |
| alternative | 2.1.2.7.2 |
| atmospheric pressure | 2.1.9.2 |
| auxiliary connections | 2.1.17.17 |
| axial load of pump rotor | 2.1.15.4 |
| axial split | 2.1.17.6 |
| В | |
| balancing rate of flow | 2.1.3.3 |
| barrel casing | 2.2.9.8 |
| barrier liquid | 2.1.17.13 |
| basic design pressure | 2.1.9.15 |
| buffer liquid | 2.1.17.14 |
| С | |
| canned motor pump | 2.1.17.18 |
| canned rotor | 2.1.17.18 |
| CCW | 2.1.14.7 |
| circulation | 2.1.17.11 |
| clearance volume | 2.3.5.1 |
| clockwise rotation | 2.1.14.6 |
| close-coupled | 2.2.9.6 |
| component | 2.1.17.27 |
| conditions | 2.1.1.5 |
| connection loads | 2.1.15.1 |
| corrosion allowance | 2.1.17.5 |
| counter-clockwise rotation | 2.1.14.7 |
| coupling | 2.1.17.24 |
| coupling service factor | 2.1.17.24.1 |
| critical speed | 2.2.6.2 |
| CW | 2.1.14.6 |
| D | |
| density | 2.1.16.1 |
| design | 2.1.2.1 |
| design axial load | 2.1.15.4.1 |
| design radial load | 2.1.15.5.1 |
| differential pressure | 2.1.9.6.1 |
| double acting | 2.3.6.2 |
| double casing | 2.2.9.7 |
| double flow | 2.2.9.5 |
| driver | 2.1.17.23 |
| driver power input | 2.1.11.3 |
| driver rated power output | 2.1.11.4 |
| dry critical speed | 2.2.6.3 |
| duty point | 2.1.13.1 |
| dynamic viscosity | 2.1.16.3 |
| F | |
| face runout | 2.1.17.10 |
| flow rate | 2.1.3.2 |
| force | 2.1.15.2 |
| G | |
| gas content | 2.1.16.5 |
| gauge pressure at point x | 2.1.9.7 |
| geometric displacement volume | 2.3.5.3 |
| geometrical flow | 2.3.1.2 |
| guarantee point | 2.1.13.2 |
| H | |
| head | 2.1.5.1 |
| head at peak point | 2.2.4.3 |
| height | 2.1.4.2 |
| height of the inlet connection | 2.1.4.3 |
| height of the inlet manometer | 2.1.4.9 |
| height of the inlet side of the installation | 2.1.4.7 |
| height of inlet-side measuring point | 2.1.4.5 |
| height of the NPSH datum plane | 2.1.5.4 |
| height of the outlet connection | 2.1.4.4 |
| height of the outlet manometer | 2.1.4.10 |
| height of the outlet side of the installation | 2.1.4.8 |
| height of outlet-side measuring point | 2.1.4.6 |
| hydraulic efficiency | 2.1.12.3 |
| hydrodynamic bearing | 2.1.17.19 |
| hydrodynamic radial bearing | 2.1.17.19.1 |
| hydrodynamic thrust bearing | 2.1.17.19.2 |
| hydrostatic test pressure | 2.1.9.14 |
| I | |
| inboard pump | 2.3.6.4 |
| injection flush | 2.1.17.12 |
| inlet area of the installation | 2.1.7.3 |
| inlet area of the pump | 2.1.7.1 |
| inlet pressure of the installation | 2.1.9.8 |
| inlet pressure of the pump | 2.1.9.4 |
| inlet rate of flow | 2.1.3.5 |
| installation | 2.1.1.3 |
| installation NPSH curve | 2.1.13.7 |
| installation total head | 2.1.1.3.1 |
| intermediate take-off rate of flow | 2.1.3.7 |
| K | |
| kinematic viscosity | 2.1.16.2 |
| L | |
| leakage rate of flow | 2.1.3.4 |
| level difference | 2.1.4.11 |
| liquid pump | 2.1.17.2 |
| local velocity | 2.1.8.6 |
| loss of head | 2.1.5.3 |
| M | |
| manifold | 2.3.6.6 |
| mass rate of flow | 2.1.3.1 |
| maximum allowable casing working pressure | 2.1.9.11 |
| maximum allowable continuous speed | 2.1.14.2 |
| maximum allowable flow | 2.1.3.2.6 |
| maximum allowable inlet pressure | 2.1.9.4.1 |
| maximum allowable temperature | 2.1.10.1 |
| maximum allowable working pressure | 2.1.9.10 |
| maximum axial load | 2.1.15.4.2 |
| maximum dynamic sealing pressure | 2.1.9.12 |
| maximum flow | 2.1.3.2.4 |
| maximum head | 2.2.4.4 |
| maximum inlet pressure | 2.1.9.4.2 |
| maximum outlet pressure | 2.1.9.5.1 |
| maximum pump power input | 2.2.3.3 |
| maximum radial load | 2.1.15.5.2 |
| maximum static sealing pressure | 2.1.9.13 |
| mean velocity at inlet | 2.1.8.2 |
| mean velocity at inlet area of the installation | 2.1.8.4 |
| mean velocity at outlet | 2.1.8.3 |
| mean velocity at outlet area of the installation | 2.1.8.5 |
mean velocity at point 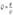
| 2.1.8.1 |
| mean velocity at throat | 2.2.6.1 |
| mechanical efficiency | 2.1.12.2 |
| minimum allowable continuous speed | 2.1.14.3 |
| minimum allowable flow | 2.1.3.2.7 |
| minimum allowable stable | 2.1.3.2.7.1 |
| minimum allowable thermal flow | 2.1.3.2.7.2 |
| minimum continuous stable flow | 2.2.1.1 |
| minimum continuous thermal flow | 2.2.1.2 |
| minimum flow | 2.1.3.2.5 |
| mixture | 2.1.16.4 |
| moment | 2.1.15.3 |
| motor efficiency | 2.1.12.4 |
| multi-phase | 2.1.16.7 |
| multi-stage | 2.2.9.3 |
| N | |
| net positive inlet pressure | 2.3.4.7 |
| net positive inlet pressure available | 2.3.4.8 |
| net positive inlet pressure required | 2.3.4.9 |
| net positive suction head | 2.1.5.5 |
| net positive suction head 3% | 2.2.4.5 |
| net suction head available | 2.1.5.5.1 |
| net positive suction head required | 2.1.5.5.2 |
| net positive suction head required for drop of 3% | 2.1.5.5.3 |
| nominal | 2.1.2.9 |
| normal | 2.1.2.5 |
| normal flow | 2.1.3.2.3 |
| NPIP | 2.3.4.7 |
| NPIPA | 2.3.4.8 |
| NPIPR | 2.3.4.9 |
| NPSH | 2.1.5.5 |
| NPSH datum plane | 2.2.2.1 |
| NPSH3 | 2.2.4.5, 2.1.5.5.3 |
| NPSHA | 2.1.5.5.1 |
| NPSHR | 2.1.5.5.2 |
| О | |
| operating | 2.1.2.3 |
| operating conditions | 2.1.2.3.1 |
| operating point | 2.2.7.3 |
| optimum head | 2.2.4.1 |
| optimum pump power input | 2.2.3.1 |
| optimum rate of flow | 2.1.3.2.1 |
| outboard pump | 2.3.6.5 |
| outlet area of the installation | 2.1.7.4 |
| outlet area of the pump | 2.1.7.2 |
| outlet pressure of the installation | 2.1.9.9 |
| outlet pressure of the pump | 2.1.9.5 |
| outlet rate of flow | 2.1.3.6 |
| overall efficiency | 2.1.12.5 |
| P | |
| parallel operation | 2.1.17.3 |
| part | 2.1.17.25 |
| peak point | 2.2.7.2 |
| piston velocity | 2.3.3.3 |
| plunger velocity | 2.3.3.3 |
| pre-charge pressure | 2.3.4.6 |
| pressure at point x | 2.1.9.1 |
| pressure casing | 2.1.17.30 |
| pressure head | 2.1.5.1.1 |
| pressure of temperature rating | 2.1.2.4 |
| pressure pulsations | 2.3.4.5 |
| product lubrication | 2.1.17.20 |
| pulsation dampener | 2.3.6.7 |
| pump | 2.1.1.1 |
| pump best efficiency | 2.1.12.1.1 |
| pump driver | 2.1.17.23 |
| pump efficiency | 2.1.12.1 |
| pump efficiency curve | 2.1.13.5 |
pump 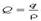 curve curve
| 2.2.7.1 |
| pump liquid | 2.1.17.1 |
| pump mechanical power losses | 2.1.11.5 |
| pump NPSH curve | 2.1.13.6 |
| pump power input | 2.1.11.2 |
| pump power input curve | 2.1.13.4 |
| pump power output | 2.1.11.1 |
| pump rated power input | 2.1.11.2.1 |
| pump total head | 2.1.5.1.3.2 |
| pump unit | 2.1.1.2 |
| pump unit total head | 2.1.5.1.3.3 |
| pumping chamber area | 2.3.2.3 |
| Q | |
| quenching | 2.1.17.15 |
| R | |
| radial load of pump rotor | 2.1.15.5 |
| radial split | 2.1.17.7 |
| rate of flow | 2.1.3.2 |
| rated | 2.1.2.2 |
| rated conditions | 2.1.2.2.1 |
| rated differential pressure | 2.1.9.6.2 |
| rated flow | 2.1.3.2.2 |
| rated inlet pressure | 2.1.9.4.3 |
| rated outlet pressure | 2.1.9.5.2 |
| rated speed | 2.1.14.4 |
| reference plane | 2.1.4.1 |
| relief-valve accumulation pressure | 2.3.4.2 |
| relief-valve back pressure | 2.3.4.4 |
| relief-valve reseat pressure | 2.3.4.3 |
| relief-valve set pressure | 2.3.4.1 |
| RL | 2.3.5.4 |
| rod load | 2.3.5.4 |
| rotodynamic pump | 2.2.9.1 |
| rotor | 2.2.9.9 |
| S | |
| seal flush | 2.1.17.11 |
| series operation | 2.1.17.4 |
| shaft deflection | 2.1.15.6 |
| shaft runout | 2.1.17.8 |
| shaft stiffness | 2.1.17.9 |
| shut-off head | 2.2.4.2 |
| shut-off pump power input | 2.2.3.2 |
| simplex, duplex, triplex, multiplex | 2.3.6.3 |
| single acting | 2.3.6.1 |
| single flow | 2.2.9.4 |
| single stage | 2.2.9.2 |
| slip flow | 2.3.1.1 |
| solid content | 2.1.16.6 |
| specific energy | 2.1.6 |
| specific speed | 2.2.8.2 |
| speed | 2.1.14.1 |
stable pump 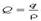 curve curve
| 2.2.7.1.1 |
| standby pump | 2.1.17.29 |
| standby service | 2.1.17.28 |
| static head | 2.1.5.2 |
| sub-assembly | 2.1.17.26 |
| submergible pump | 2.1.17.22 |
| submersible pump | 2.1.17.21 |
| suction-specific speed | 2.2.8.3 |
| swept volume | 2.3.5.2 |
| system | 2.1.1.4 |
| T | |
| test | 2.1.2.8 |
| throat area | 2.2.5.1 |
| throttle bush | 2.1.17.16 |
| total head | 2.1.5.1.3 |
| trip speed | 2.1.14.5 |
| type number | 2.2.8.1 |
| U | |
unstable pump 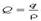 curve curve
| 2.2.7.1.2 |
| V | |
| valve seat area | 2.3.2.1 |
| valve seat velocity | 2.3.3.1 |
| valve spill area | 2.3.2.2 |
| valve spill velocity | 2.3.3.2 |
| vapor pressure of the pumped liquid | 2.1.9.3 |
| velocity head | 2.1.5.1.2 |
| velocity pressure | 2.1.9.16 |
| volume rate of flow | 2.1.3.2 |
| volumetric efficiency | 2.3.5.5 |
| W | |
| wet critical speed | 2.2.6.4 |
| working | 2.1.2.7.1 |
Библиография
[1] ISO 80000-1 Quantities and units - Part 1: General (Величины и единицы. Часть 1. Общие положения)
| УДК 621.67-216.74:006.354 | МКС 23.080 | Г 82 | IDT |
| Ключевые слова: насосы, насосный агрегат, термины и определения, физические величины, напор, подача, кавитационный запас, коэффициент быстроходности |
Электронный текст документа
подготовлен АО "Кодекс" и сверен по:
официальное издание
М.: Стандартинформ, 2015