SECTION 1. FAMILY LIFE
Module 1. Family Relationships and Kinds of Family
Exercise 1. Read and translate the following text. Answer the questions after the text.
The Role and Functions of a Family
Family is the basic unit of social organization in all human societies. Since prehistoric times, families have served as the primary institution responsible for raising children, providing people with food and shelter, and satisfying people’s need for love and support. The term family generally refers to a group of people related to one another by birth, marriage, or adoption. In contemporary society, people often apply the word family to any group that feels a sense of kinship (family connection).
Family types vary in different countries and among different cultures. In Western, industrialized societies, the nuclear family ranks as the most common family type. It consists of a father, a mother, and their children.When the unit includes a husband and wife, it is considered a conjugal family as well. Nuclear and conjugal families as isolated and independent units are very rare in the world. In most societies the extended family is the norm. This type goes beyond the nuclear family unit of parents and children to include relatives such as grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins. When, for example, a married couple lives with the husband's parents or a grandparent shares a household, the family changes from a nuclear to an extended one. The addition of any persons beyond the nuclear unit makes the family extended.
American families typically have what is called a modified extended family structure. When couples marry they are likely to form a household separate from either set of parents. Yet they maintain close ties with their families of orientation. While the newly created nuclear family units do not reside in an extended family household, they do exchange phone calls, letters, and holiday or birthday greetings and turn to one another for assistance. In this sense a nuclear family becomes a modified form of an extended one though not in terms of residence.But nuclear families exist alongside many other types of family units. In the single-parent family, for example, a mother or a father heads the family alone. A blended family, also known as stepfamily or reconstituted family, is formed when a divorced or widowed parent remarries. As divorce rates have risen, the number of single-parent and blended families has increased.
An increasingly common family form in Western societies is the consensual union, in which couples live together but remain unmarried. When a homosexual couple decides to live together as a family, they form a same-sex union. Although such unions have become more common, most countries do not recognize them as legal families. People often call a married couple whose children have grown up and left home an empty-nest family.
In many parts of the world, parents and children live together with other family members under the same roof. These complex families usually contain several generations of family members, including grandparents, parents, and children. They may also include brothers or sisters and their families, uncles, aunts, and cousins. Even when relatives do not live together, they still consider themselves members of the same extended family. In Latin American and Hispanic American cultures, the extended family, or la familia, includes grandparents, uncles, aunts, and cousins.
Some cultures follow a traditional practice called polygamy, in which a person can have more than one spouse (husband or wife). The two chief forms of polygamy are polygyny and polyandry. In polygyny, a man marries more than one woman. In polyandry, a woman has more than one husband.
Family members can be related to one another by blood – that is, by birth; by affinity – that is, through marriage; or through adoption. Most nuclear families consist of a father, a mother, and their biological children (children born to them). When a couple adopts a child, the child becomes a member of their family. Brothers and sisters who share the same parents are siblings. Half brothers and half sisters share either the same biological mother or biological father. When divorced or widowed parents remarry, the parent’s new spouse becomes the children’s stepfather or stepmother. Children from the couple’s previous marriages become stepbrothers and stepsisters to one another.
When people marry, they gain a new set of relatives called in-laws. The mother of a person’s spouse is called a mother-in-law, the brother is called a brother-in-law, and so on throughout the rest of the family.
The parents of a person’s mother or father are that person’s grandparents. Great-grandparents are the parents of a person’s grandparents. An aunt is the sister of a person’s mother or father. An uncle is the brother of a parent. An uncle’s wife is also called aunt, and an aunt’s husband is also called uncle. A first cousin is the child of a person’s aunt or uncle. The child of a first cousin is a person’s first cousin once removed – that is, removed by one generation. Children of first cousins are second cousins to each other.
Some people consider certain friends as part of their family because they feel special affection for them. Though these friends are not true family members, such friends are called fictive kin, and family members might call them “aunts” or “uncles”. Relatives or close friends of a parent may become godparents to that parent’s children. Godparents, as sponsors to a Christian baptism, often play more vital roles in the lives of families than other fictive kin. In Latin American and Hispanic American families, godparents, or compadres, provide advice, emotional support, and assistance in times of need.
Families perform many necessary functions, both for individual family members and for society as a whole. In virtually all cultures, the family serves as the basic institution for bearing children, caring for them during their early years, and preparing them to function effectively in society. Families around the world must also provide food and clothing to their members. In addition, families meet important psychological needs, such as the need for love, support, and companionship.
The family’s duties have changed over time. In the past, families not only cared for the young but also grew their own food, made their own clothing, and provided services for themselves that modern families generally do not provide. Parents taught reading, writing, and craft skills to their children. Families also cared for sick and elderly relatives and often provided financial support for members in need. Since the 1800’s, many of these traditional responsibilities have shifted to such institutions as schools, hospitals, insurance companies, and nursing homes.
Roles within the family have also changed. Traditionally, the father was expected to take up an occupation to support his wife and children. The mother, in turn, ran the home and cared for the children. Today, however, both parents commonly work outside the home, and fathers often perform household duties formerly expected of women.
The home is the center of family activities. These activities include raising children, eating meals, playing games, watching television, keeping house, and entertaining friends. In the home, children learn basic social skills, such as how to talk and get along with others. They also learn health and safety habits there. A family’s home life is influenced by which members live in the home and by the roles each member plays. Home life can also be affected by relatives who live outside the family’s home. Traditions, laws, and social conditions help determine who lives in a home and the place each family member holds.
Traditions, which are customs or beliefs that people have followed for a long time, strongly influence family life. For example, some Americans have little contact with relatives outside the nuclear family. But many Chinese families feel strong ties to such relatives and see them often. Aunts, uncles, and cousins traditionally play important roles in the lives of these people.
Laws affect family behavior in various ways. Some set forth the legal rights and responsibilities people have as husbands, wives, parents, and children. In many Western nations, laws forbid abuse of children by parents, and of one spouse by the other. Laws also deal with marriage, divorce, and adoption. Social conditions can also influence family life. For example, in cultures that discourage women from working outside the home, mothers become full-time homemakers, while men act as the sole wage earners.
(Steven Mintz, Ph.D., Associate Professor of History, University of Houston.)
Questions:
1. What is the role of the family in modern society? 2. What responsibilities do parents have toward their children? 3. How many different types of family do you know? 4. What is a nuclear family (single-parent family, blended family, consensual union, same-sex union, empty-nest family, extended family)? 5. In what countries does an extended family type still predominate? What type of family is the most characteristic one for your country? 6. What is the difference between polygynyand polyandry? 7. What cultures follow polygamy? 8. How can family members be related to one another? 9. What is the difference between siblings and half-brothers or sisters? 10. How are second cousins related to each other? 11. Who are in-laws? 12. Whom do we call fictive kin? 13. What are the functions the family fulfills in society? 14. How have these functions changed over time? 15. How have traditional family roles changed? 16. What laws regulate relations within a family?
Exercise 2. Find in the text equivalents to the following words and word combinations.
1. a structure or building that provides cover from weather or protection against danger; 2. legal procedure for taking a child into the family from an orphanage; 3. two people who are married, are living together; 4. somebody’s husband or wife; 5. the custom of having more than one spouse at the same time; 6. a relative by marriage; 7. somebody who is named as a sponsor when a child is baptized; 8. skill in making or doing things, especially by hand; 9. the people who live together in a single home; 10. the ending of a marriage by an official decision in a court of law; 11. the only one.
Exercise 3. Read the short article about British and American families. Choose the best phrase from A-K to fill in the gaps 1-10, to complete the text. There is one phrase that you won’t need to use.
| FAMILY WHEN British and American people use the word family (1) … the mother, father and their children. In a general social context, “the family” is usually (2) … mean this nuclear family. Society in Britain and the US (3) … a nuclear family living in the same house and (4) … each other’s lives. Fifty years ago, the typical family was a husband and a wife, and two or three children. The father spent all day at work and (5) … decisions about how the money he earned was spent. The mother stayed at home to manage the house and look after the children. Children were (6) … their parents. Many modern families live rather differently, and because of this some people think that the family unit is dying and society (7) …. Many couples still get married, but others live together without (8) …. A few years ago, couples living together usually got married when (9) … a family, but this happens less now. Another trend is (10) … married later in life and to have fewer children, so the size of the average family is shrinking. |
A taken to G made most of the
B closely H which normally consists of
C getting married I they wanted to start
D they often mean only J expected to obey
E is being weakened K is traditionally based on
F for people to get
Read the article again and answer the following questions:
1. What is a ‘nuclear family’?
2. How did the father spend a typical day fifty years ago?
3. How did the mother spend a typical day fifty years ago?
4. Why are some people worried about society today?
5. Do couples that live together always get married?
6. Are modern families normally larger or smaller than those fifty years ago?
Exercise 4. Fill in suitable words:
1. Your aunt’s son is your …. 2. Your father’s father is your …. 3. My sister’s son is my …. 4. His sister’s daughter is his …. 5. My mother’s brother is my …. 6. Your mother’s sister is your …. 7. Your father’s brother is your …. 8. Your uncle’s daughter is your …. 9. Your brother’s wife is your …. 10. Your sister’s husband is your …. 11. Your husband’s mother is your …. 12. Your mother’s mother is your ….
Exercise 5. What is the difference in meaning between the following?
1. Parents and relatives
2. Nephews and nieces
3. Stepsisters and sisters-in-law
4. Godfathers and great-uncles
5. Brothers and cousins
6. A close relative and a distant relative
Exercise 6. Complete the sentences with the words denoting relationships. Mind that some words DO NOT show family bonds.
1. Our mothers are sisters. We are ….
2. We share an office. We are ….
3. My parents are divorced My dad has just married Clair’s mum. Clair and I are ….
4. We had our anniversary last week. We are ….
5. I am married to Mary’s brother. Mary and I are ….
6. We share a flat. We are … /
7. We sit next to each other at school. W are….
8. We live next door to each other. We are ….
9. My sister has a son and a daughter. They’re my … and ….
10. We write to each other but we’ve never met. We are ….
Exercise 7. Choose the most suitable word or phrase to complete the sentence below.
1. Mrs Jones had ….
a. trio b. a treble c. triplets
2. Mrs Vine had had … the week before.
a. quarts b. quads c. a quartet
3. Twins often seem to … a generation.
a. hop b. skip c. jump
4. There was a case of … twins in our town recently.
a. Japanese b. Chinese c. Siamese
5. There’s a … of twins in our family – on my father’s ….
a. story b. geography c. history
d. tree e. side f. line
6. I was … child, though.
a. an only b. a missing c. a single
7. All the members of our football team are related … marriage.
a. by b. to c. on
8. When Mother remarried, her second husband, my …, gave me a new bicycle.
a. forefather b. stepfather c. grandfather
9. He said to me, ‘Look, I know you’re not my own …, but let’s be friends.’
a. flesh and blood b. blood and guts c. skin and bones
10. My … originated from a tribe of Red Indians.
a. ancestors b. ancients c. antiques
11. Not many of my own … relatives are still alive.
a. blood b. skin c. heart
12. My … -grandfather fought at the Battle of Waterloo.
a. grand grandgrand b. great grand grand c. great-great-great
13. My brother-in-law inherited £500,000 in his uncle’s ….
a. will b. testament c. wishes
14. I was left £50 and a cat by … relative; I believe it was a … cousin – or perhaps it was a … aunt.
a. a distant b. an unclear c. a long-distance
d. double e. second f. dual
g. grand h. great i. large
15. Peter is an orphan; he was … at the age of two.
a. adjusted b. adapted c. adopted
16. Paul comes from a broken home; he has lived with a number of … parents.
a. loan b. foster c. second-hand
17. Mary was from a single-parent family; now she’s looked after by her ….
a. keeper b. warden c. guardian
18. I’m off to have Sunday lunch with my new … now.
a. outlaws b. by-laws c. in-laws
Exercise 8. Fill in the blanks. The first letter of each missing word is given.
A nuclear family consists of only a (1) h…, (2) w… and children. In my country an (3) e… family is more common. It consists not only of (4) p… and children but also of (5) g…, aunts, uncles and (6) c…. My (7) g… lives with us and loves looking after her grandchildren. My mom’s brother, (8) U… George, is a (9) w… and has lived with us since since Aunt Helen died. He is also my godfather.
Exercise 9. Read the clues and complete the crossword.
The Andrews family tree
Jack Andrews + Daisy
Lucy Emily + George
Michael Susan (Rupert)
Bianca Robbie
| ACROSS | |
| 1Susan’s parents, Emily and George, are Australian. Jack is her …. | 7Susan’s engaged. Her … is called Rupert. He is twenty-two and he is a computer programmer |
| 2Jack emigrated to Australia and married Daisy. Daisy is Susan’s …. | 8Rupert’s mum died when he was at university and so Rupert’s dad is a …. |
| 3They had another daughter, Lucy – so Emily has a sister. Lucy is Susan’s …. | 9Rupert’s dad is getting married to Maria soon, and Maria will be Rupert’s …. |
| 4When Susan’s brother Michael got married, he had two children, Bianca and Robbie. Now Susan has a niece and a …. | 10When Susan and Rupert get married,Rupert’s dad will beSusan’s…. |
| 5Susan’s dad died a few years ago and her mum became a …. | 11Bianca is Jack and Daisy’s …. |
| 6Emily remarried and her new husband Bill, is a lawyer. Bill is Susan’s …. | 12Robbie is Michael’s …. |
| DOWN | |
| 1What are Susan’s … called? |
Exercise 10. Read the sentences below. Sally is describing her relationship with people in her family. Match the underlined phrase with the best definition below.
1. I look like my dad.
2. I take after my mum.
3. I get on (really) well with my cousin, Jake.
4. I’ m very close to my twin sister, Karen.
5. I have a lot in common with my brother, Will.
6. I ’m (a bit) like Aunt Gillian.
7. I am totally devoted to her grandfather.
8. I care for my elderly parents.
9. I often turn to my sister for advice.
10. My brother gets on my nerves.
11. I don’t like being left out.
12. My mother tells me off when I amill behaved.
I have a similar personality.
I have inherited some of her characteristics.
I am very loving and loyal.
I am angrily criticised.
I have a very good relationship.
We share similar interests.
I feel deep concern and interest/do everything for those who need help.
I have a similar appearance.
I go for help in a difficult situation.
I have a deep, strong relationship.
I feel annoyed.
I feel ignored and neglected.
Now use the underlined phrases in the exercise above to best describe the following relationships.
1. John and Rob really enjoy each other’s company, because they both love playing football, talking about cars, and going out.
2. Claire has lots of friends, but if she has a problem to solve or a secret to share she always tells her cousin, Sue, first. They grew up together, and can trust each other completely.
3. Whatever I do, my Dad is saying I was wrong or not good enough.
4. My Aunt Rose has the same long nose and high cheekbones as my mum. People often mistake her for her sister.
5. Molly is so loyal to her old Granny that she refuses to send her to the old peoples’ home and looks after her herself. (2)
6. My nephews, Paul and Colin, are both very talkative and outgoing.
7.In my childhood I ran to my Aunt Sara each time I were in trouble and needed help.
8. My mum tells me that I get my fiery temper and stubborn nature from my granny.
9. Her little sister is so naughty and loud that she annoys me every time I come to see my friend Joan.
Exercise11. There are many idiomatic expressions in English to describe family relationships. Divide the phrases into two groups: people are similar, and people are different.
We’re as different as chalk and cheese.
We’re like two peas in a pod.
We get on like a house on fire.
She’s the spitting image of her mother.
I have little to do with her.
You just can’t tell them apart.
Speak on your family members using these idioms.
Exercise 12. Work with a partner. Ask him/her the following questions and make a note of his/her answers.
| QUESTIONS | ANSWERS |
| How many children, including you, are there in your family? | |
| Are you the oldest child, the youngest child, or somewhere in the middle? | |
| What is the age difference between the oldest child and the youngest? | |
| What do you think is an ideal number of children to have in a family? | |
| What is an advantage of your position in the family? | |
| What is a disadvantage of your position in the family? |
Look at the answers that you got from your partner and compare them with the answers he/she got from you. How many of your answers are the same? How similar are your families?
Exercise 13. Read the abstracts and explain and study the bolded words. Check them in the dictionary if necessary.
Father and son
| I take after my father. We are both tall – that runs in the family– and we both have a passion for the outdoor life. I was brought upon a farm and always looked up tomy father, so it was no surprise when I followed inhis footstepsand joined him on a family farm. Basically farming is in my blood, and it’s been our way of lifefor five generations. Working with Dad is great. He knowsthe business inside out, and enjoys showingme the ropes. And from hispoint of view, he likes to have someone younger with new ideas – even if they aren’t that good! |

|
Complete the sentences with the correct preposition.
1. He hopes to follow … my footsteps.
2. She has a different point … view.
3. Politics is … my blood.
4. Baldness seems to run … my family.
5. It’s a different way … life.
Complete the text.
My father was a classical pianist. He knew the works of Mozart inside (1) … and performed them all over the world. He (2) … me up to love music as well; it seems to be something that (3) … in our family. However, I eventually (4) … in my mother’s footsteps and became a doctor, and, by coincidence, it was my uncle (my mother’s brother) who showed me the (5) … when I got my first job in aa hospital in London.
Supply the phrase to each definition.
1 respect and admire smb
2 the behaviour and customs that are typical of a person or a group
3 be found very often in a family
4 (inf) show smb carefully what to do and how to do it
5 a way of looking at a situation; an opinion
6 care for and teach a child until they are an adult
7 be a strong part of one’s character
8 have a lot of knowledge of smth
9 do the same job or activity as smbelse who did it before you
(from Idioms and Phrasal Verbs)
Exercise 14. Try to make a list of all the members of your family: cousins, aunts, uncles, etc. Compare your list with your partner’s. Tell your group-mates about your family and your distant and close relatives both on your father’s and your mother’s sides. Tell your partner the following:
Who do you take after? In what ways?
Who do you get on really well with in your family? In what ways?
Apart from your close family, do you keep in touch with any distant relatives?
| Video |
1. How many families are there in the video? What are their names?
2. In the first couple, where does she come from? What information does she tell us about her village?
3. In the second family, what happened with their son? What is the punishment to the boy?
4. In the third family, where are they coming from with a baby? Why Mitchell talk to everybody in the plane?
5. What happened in the garden? Did the father finally shoot his son?
6. What is the pink wall?
7. Do you think the three families know each other?
8. How many people are in each family?
Exercise 16. Supply the missing words.
1. My sister’s husband is my ….
2. His parents are his children’s ….
3. Your mother’s sister is your ….
4. My uncle’s brother is my ….
5. His wife’s sister is his ….
6. My mom is my son’s ….
7. His sister’s daughter is his ….
8. My uncle’s daughter is my ….
9. His son and daughter are his sister’s ….
10. My husband’s mother is my ….
11. Her aunt’s sister is her ….
12. His daughter is his mother’s ….
13. Her brother’s son is her ….
14. My son and daughter are my parents’ ….
15. His wife’s dad is his ….
16. Your father is your daughter’s ….
17. My father’s brother is my ….
18. Your son is your dad’s ….
19. My Aunt’s son is my ….
20. Your mom’s sister and her husband are your ….
| Video |
Exercise 17.
1. Complete the table from the words and phrases in the box.
| ancestor | battle | Chancellor |
| descendant | distant relative | dynasty |
| general | House of Commons | House of Lords |
| Member of Parliament (MP) | orator | paternal grandfather |
| prime minister | soldier | speech |
| Family | Politics | War |
2. Work with a partner and discuss the questions.
· What do you know about Winston Churchill?
·

|

|
3. You are going to watch a video about Churchill’s life. Which of the words in the box below do you expect to hear?
| duke | Glastonbury Festival | illness |
| MP | Nobel Prize | Princess Diana |
| school | Second World War | wealthiest |
4. Watch again and complete the sentences.
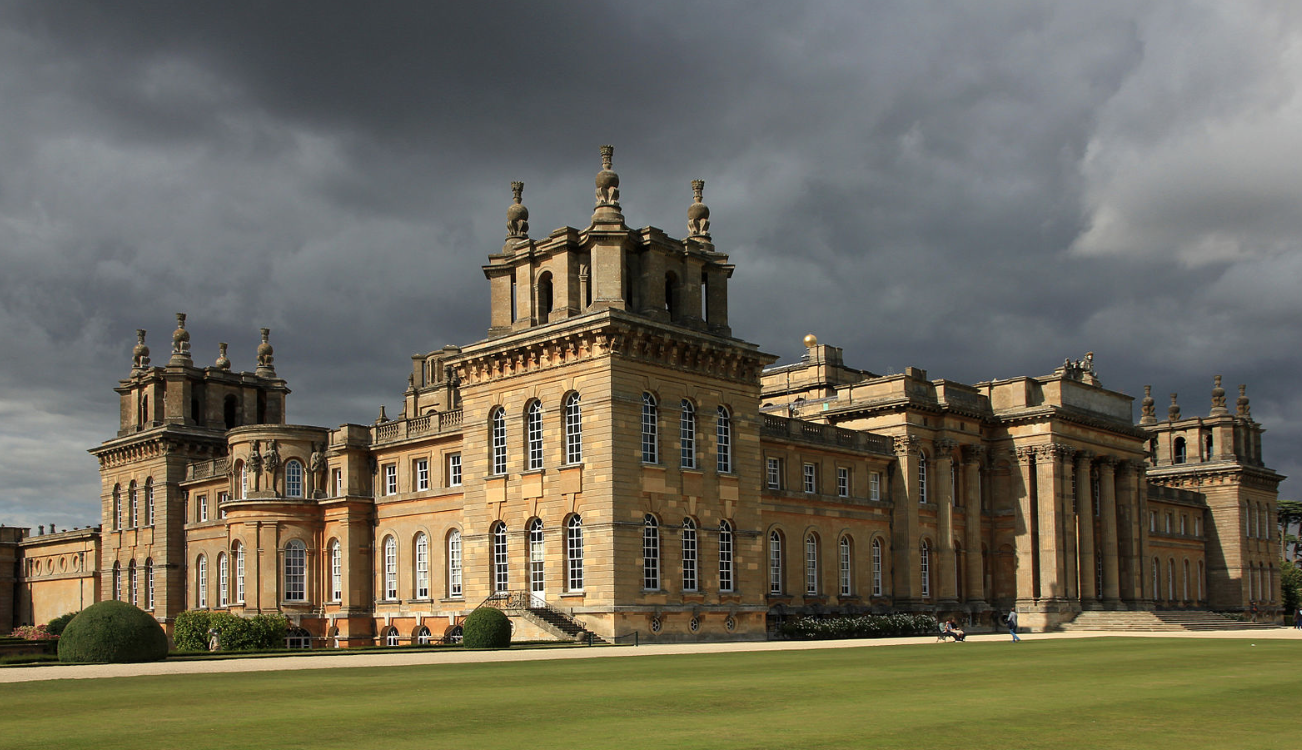
1. Blenheim Palace was built for Winston Churchill’s ancestor John Churchill as a reward for …
2. Winston’s father, Randolph Churchill, held a number of political positions, including Leader of …
3. Winston’s mother, Jennie, came from …
4. Winston didn’t have a close relationship with …
5. Winston Churchill was prime minister during …
6. Winston Churchill is particularly famous for making …
7. Winston Churchill won a Nobel Prize for …
Exercise 18. Read and translate the text.
Genealogy has had a surge of popularity over the last 30 years. However, it has continuously been of interest and importance to people for hundreds of years. Those of noble birth in the European courts especially needed to know their lineage to determine who was actually in line for the crown.
The term ‘genealogy’ is the study of family ancestors with documentation of birth, marriage and death dates through parents, grandparents, great grandparents, as far back as possible. Whereas, ‘family history’ is more an in-depth study of the lineage in a family including the life stories of individuals; like their education, occupations, medical conditions, military service, residences, etc.
|
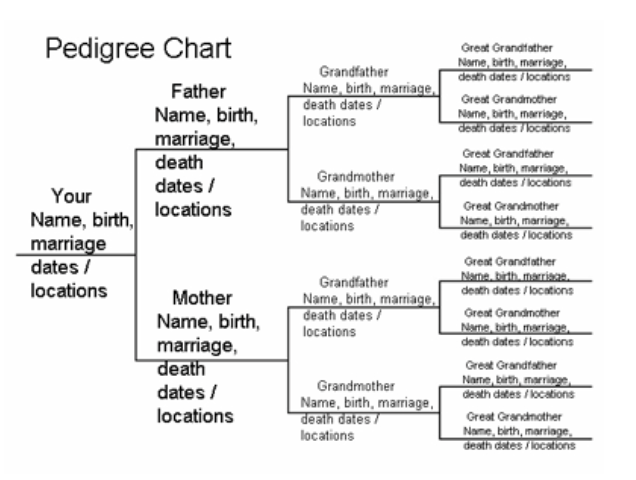
A pedigree chart or listing of each person with the basic information is essential. The key is beginning with oneself. Write out your name, birth date, birth location, marriage date and location. Draw two lines out or in two boxes, and place your parents’ names. Add their birth, marriage and death dates along with locations. Now this is the initiation of a family tree.
From each of your parents, is another line or box for their mother and father; they would be your grandparents. This is forming a direct lineage of your ancestors (parents > grandparents > great grandparents, etc.).
Today, there are numerous reasons to research one’s genealogy and expand it as a full family history. First, is for a medical family history. With the knowledge of genetics, medical science needs to know an individual’s family history; what one’s parents, grandparents, aunts or uncles suffered or died from assists the doctors to better know how to prevent and treat you, the descendant, as an individual today.
Secondarily, discovering the geographical and historical time periods of ancestors provides a better perception of what shaped their lives. If one was living in the rural English countryside of the Lake District in the1880s, their farm life focused on the four seasons. It would be a different lifestyle for those living in west central England and working in Manchester’s industrial factories.
There are diversities between genealogy and family history, yet both are dependent on each other. The main lineage of a family is the heart of genealogy. You need a listing of the ancestors; names, places and dates. This creates the facts from which to build. Then, learning about each ancestor as a person; their strengths or their weaknesses, their abilities and their achievements, in a sense, puts a real face to that ancestor’s name. You might not have an image, but you can get an impression of who they were by learning more about each person.
(www. https://www.familytree.com/learn/what-is-genealogy)
Are those statements true (T) or false (F). If they are false, correct them.
Genealogy appeared 30 years ago. T/F
Genealogy studies family ancestors. T/F
To study one’s family ancestors one needs to know their official names. T/F
People study their genealogy out of pure fascination. T/F
Family tree helps to understand who you are. T/F
Answer the following questions:
What are the data one uses to study one’s genealogy?
Is there any difference between genealogy and family history?
What is a pedigree chart? How do you work it out?
Why it is important to know the lineage of your ancestors?
| Listening |
Exercise 19. Listen to AJ Jacobs talking about the world’s largest family reunion. Using genealogy websites, he's been following the unexpected links that make us all, however distantly, related. His goal: to throw the world's largest family reunion.Fill in the gaps in the sentences below.
1. The man who called AJ introduced himself as his ….
a. 2nd cousin b. 12th cousin c. 20th cousin
2. AJ thought the caller was ….
a. a fraud b. his long-lost relative c. his cousin who was kidding him
3. The World Family tree on Geni.com website includes … people.
a. 7.5 million b. 75 million c. 175 million
4. There are … links between AJ and Gwyneth Paltrow.
a. 7 b. 17 c. 70
5. Barack Obama is AJ's aunt's fifth great-aunt’s husband’s father’s wife’s seventh ….
a. great cousin b. grandson c. great-nephew
6. The scientific value of studying one’s family tree includes the data about … diseases.
a. appearance of new b. the ways of treating c. hereditary
7. AJ’s son is … years old.
a. 7 b 11 c. 17
8. Adam and Eve are our great- … times grandparents.
a. 70.000 b. 7.000 c. 170.000
9. Knowing one’s ancestors will help to stop ….
a. war conflicts b. killing different species c. racial and social discrimination
10. The family reunion AJ is planning is going to take place at the ….
a. NY Hall of Science b. World’s Fair Committee c. Global Family Reunion
Organisation
Exercise20. TranslateintoEnglish.
Это самое дорогое, что у вас есть. Это ваши мама и папа, сестры и братья, бабушки и дедушки – самые близкие вам люди, которые вас любят, заботятся о вас, делают все, чтобы жизнь ваша была счастливой. Словом, это ваша семья. Вы вырастете, полюбите, женитесь или выйдете замуж, у вас появятся дети – и родится новая семья.
Семья – самая необходимая ячейка в обществе. Стоит ли доказывать, что это так? И все же давайте вместе подумаем: чем мы все обязаны семье? Наверное, прежде всего тем, что существуем. Мы появились на свет потому, что наши мама и папа полюбили друг друга и создали семью. Значит, главное предназначение семьи в том, чтобы не иссякал человеческий род, чтобы появлялись новые люди.
Рождение ребенка – это и большая радость, но и большая ответственность. Ведь он еще совсем беспомощный, и его надо вовремя накормить, помыть, сменить одежду. Родители учат его ходить, говорить, рассказывают ему сказки, играют с ним, гуляют, знакомят с окружающим миром. В школьные годы семья помогает детям учиться, находить свое место в коллективе одноклассников. Родители и другие взрослые члены семьи пробуждают в ребенке чувства совести и справедливости, знакомят с правилами поведения в обществе и нормами морали. Они учат его быть честным, не брать чужого, уважать старших, любить Родину, ценить труд людей и многому, многому другому. Следовательно, семья нужна еще и для того, чтобы помочь ребенку стать достойным человеком и гражданином своей страны.
И, наконец, семья испокон веков считалась хранительницей домашнего очага, здорового образа жизни. В кругу родных вы находите то тепло человеческих отношений, взаимопонимание и сочувствие, которые не всегда можно найти даже среди близких друзей.
Exercise 21. Match each expression (a-j) with one of the explanations (1-10).
| a) nearest and dearest b) newlyweds c) the nuclear family d) adults e) a community f) a generation g) contemporaries h) an extended family i) a household j) outcasts | 1. people who are alive at the same time or e.g. attend the same school 2. people who’ve recently been (or are still) on the honeymoon 3. all the people of approximately the same age 4. the people in a family who live together under the same roof 5. the entire range of relatives in one family 6. all the people living together in the same area 7. a person/people from your immediate family 8. people who are no longer teenagers 9. people abandoned by their families or by society in general 10. parents and their children |
Exercise 22. Improvise the dialogues following the situations.
Situation: You are actors and you are on a casting for a play in the London West End Theatre. The plot is about a family, their friends and their daily life.
Pick up a situation and create a dialogue of 1-2 minutes that you will improvise in front of the jury. You have 1-2 minutes to prepare.
1. Mum gets home. Dad hasn't prepared the dinner. Mum is hungry and furious. Dad is embarrassed and not at ease.
2. Mum has spent the whole day on Ebay, doing some Internet shopping. When Daughter comes back from school she sees that the house is a mess. She and Mum have an argument about Internet shopping. They are both angry.
3. Uncle comes to visit the family. He and his Niece disagree about the question of social networks. Uncle is for and the Niece is against. They are calm but enthusiast about the topic.
4. Mum and Dad are having a row about buying a firewall for their computer. Mum thinks that this is useless, Dad thinks is necessary. They are angry but try to get along.
5. The family has only one computer. The Brother wants to play the video game Football Manager. The Sister wants to watch an episode of Breaking Bad, her favourite series. The Brother is yelling at his Sister. She is upset and cries.
6. The dog has eaten the Internet wire (cable). Mum cannot do her Internet shopping. The son cannot play video games online. They are very sad and they are complaining about their problem.
7. Mum and Dad want to watch a movie. They have to decide which movie to order online.
8. The printer is broken. Dad accuses his Daughter but she denies. He is furious and she is frustrated.
9. The Daughter has invited her boyfriend for dinner. Dad is not very friendly with him and keeps asking questions. The boyfriend is embarrassed but stays cool and nice.
10. Mum has put a password on the computer. The Son needs to use the computer for his homework. He calls Mum (who is at work) and tries to convince her to tell him the password. She tells him to wait her from work.
11. It is Grandma's birthday. Mum offers an I-pad to Grandma. They are both very happy and excited. But the Son is not happy because he thinks that Grandma does not know how to use the I-pad.
Exercise 23. Read and translate the text, explain in your own words the meaning of words and word combinations in bold type. Answer the questions after the text.